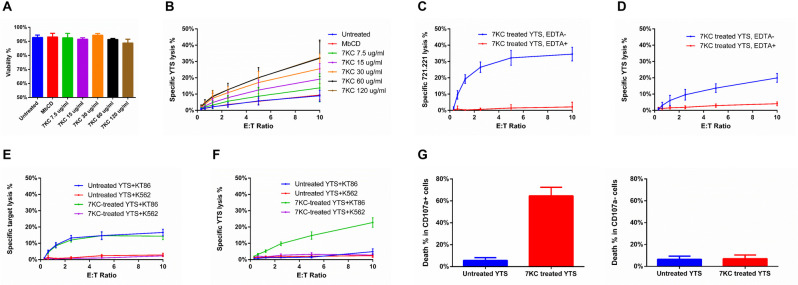
Fig 3. 7KC-induced NK cell death requires target cell–induced NK cell degranulation.
(A) Survival of YTS cells after a 4-h incubation in the absence of target cells over a range of 7KC concentrations was measured based on their uptake of PI by flow cytometry to evaluate any direct toxicity of 7KC. (B) The same range of 7KC concentrations was also used as pretreatment of 51Cr-labeled YTS cells that were incubated with 721.221 target cells over a range of effector to target cell ratios for 4 h. The release of 51Cr was measured in both sets of experiments at 4 h. Cytotoxicity (C, p < 0.05) and survival (D, p < 0.05) of 7KC-pretreated YTS cells, with or without EDTA (10 mM) calcium chelation, were measured after a 4-h incubation with 51Cr-labeled 721.221 target cells. Cytotoxicity mediated by (E, p < 0.05) and survival (F, p < 0.05) of 7KC-pretreated YTS cells were measured after a 4-h incubation with nontriggering K562 cells or triggering KT86 cells. Viability (G) of untreated and 7KC-pretreated YTS cells with or without up-regulated LAMP-1 after a 4-h incubation with 721.221 cells was evaluated using flow cytometry with PI used to detect cell death. All data represent averages from 3 independent experiments, and error bars show ± SD (A−E). Wilcoxon signed rank test was used for the comparison between curves. NK, natural killer; PI, propidium iodide; 7KC, 7-ketocholesterol.