Extended Data Fig. 7|. The H3K27me3-binding-defective mutation of BAHCC1BAH decreases overall occupancy of BAHCC1 at H3K27me3-bound genes, leading to their concurrent derepression.
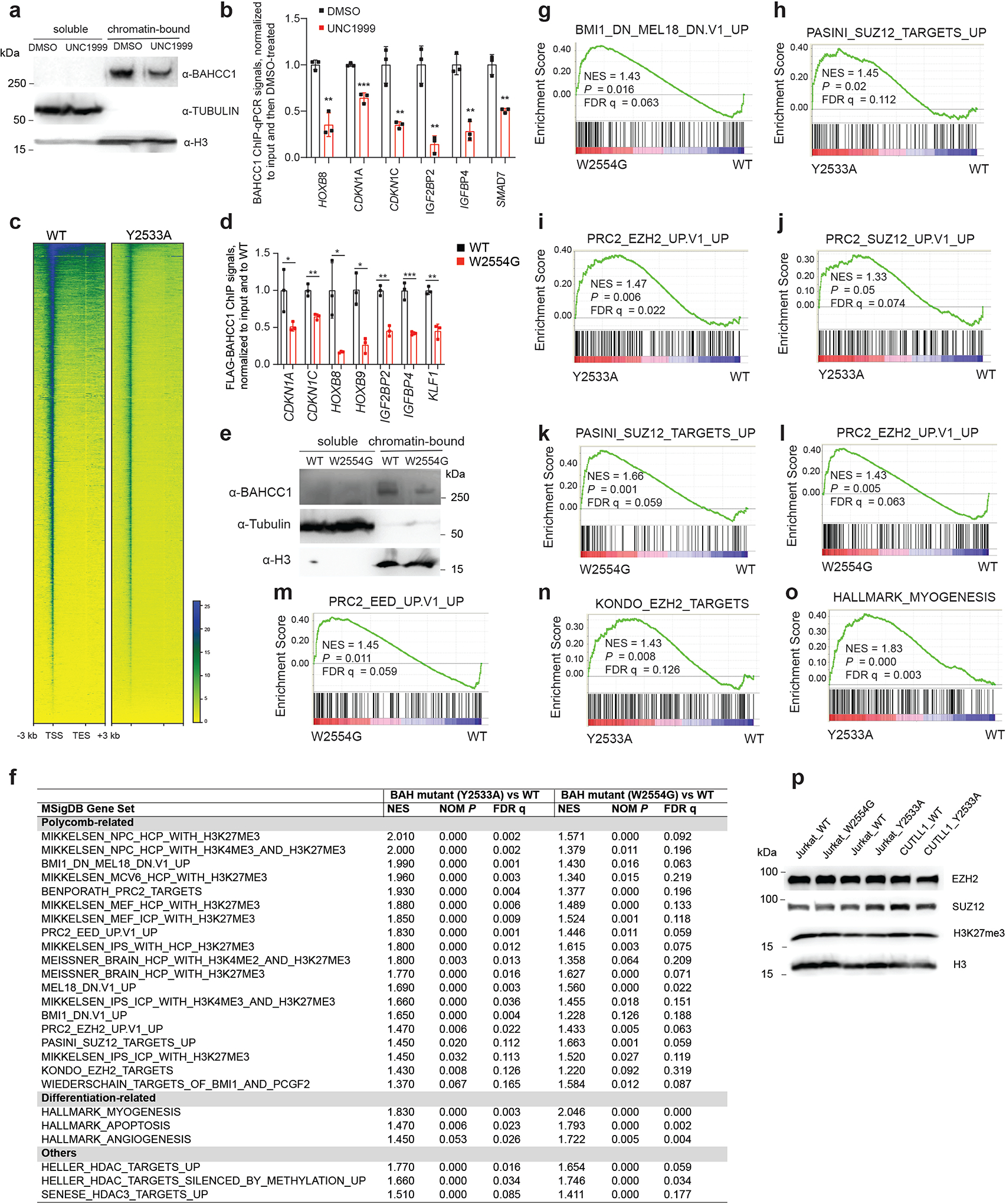
a, Immunoblots of BAHCC1, Tubulin and histone H3 using chromatin-bound and soluble fractions of 293 cells post-treatment with DMSO or UNC1999.
b, Flag ChIP-qPCR to examine binding of endogenous 3×Flag-BAHCC1 to TSS of the indicated gene in JURKAT cells post-treatment with UNC1999 versus DMSO. Data of three independent experiments are plotted as mean ± SD after normalization to those of input and to DMSO-treated. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
c, Heatmap of Flag-BAHCC1 ChIP-seq signals across all genes in JURKAT cells carrying either WT or the Y2533A homozygous mutation of 3×Flag-BAHCC1 (endogenous).
d, Flag ChIP-qPCR to examine the endogenous Flag-BAHCC1 binding to TSS of the indicated gene in JURKAT cells that carry either WT or the W2554G homozygous mutation of BAHCC1. Data of three independent experiments are plotted as mean ± SD after normalization to those of input and to WT. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
e, Immunoblots of BAHCC1, Tubulin and H3 using chromatin-bound and soluble fractions of JURKAT cells carrying WT or the W2554G homozygous mutation of BAHCC1BAH.
f, Summary of GSEA using RNA-seq profiles of JURKAT cells carrying an indicated H3K27me3-binding-defective mutation of BAHCC1BAH and their WT counterpart cells. Representative genesets showing the most significant correlations to Y2533A (left) or W2554G (right) homozygous mutation of BAHCC1BAH, relative to WT, are categorized into Polycomb-related, differentiation-related or others.
g-o, GSEA reveals that, relative to WT, the H3K27me3-binding-defective mutation of BAHCC1BAH is positively correlated to derepression of gene signatures related to PRC1 (g), SUZ12 (h, j, k), EZH2 (i, l, n), EED (m) or myogenesis (o).
p, Immunoblotting of EZH2, SUZ12, H3K27me3 and H3 in the indicated cell lines with WT or the H3K27me3-binding-defective mutation of BAHCC1BAH.
