Fig. 6. BAHCC1 interacts with corepressors, maintaining a hypoacetylated chromatin state at target genes.
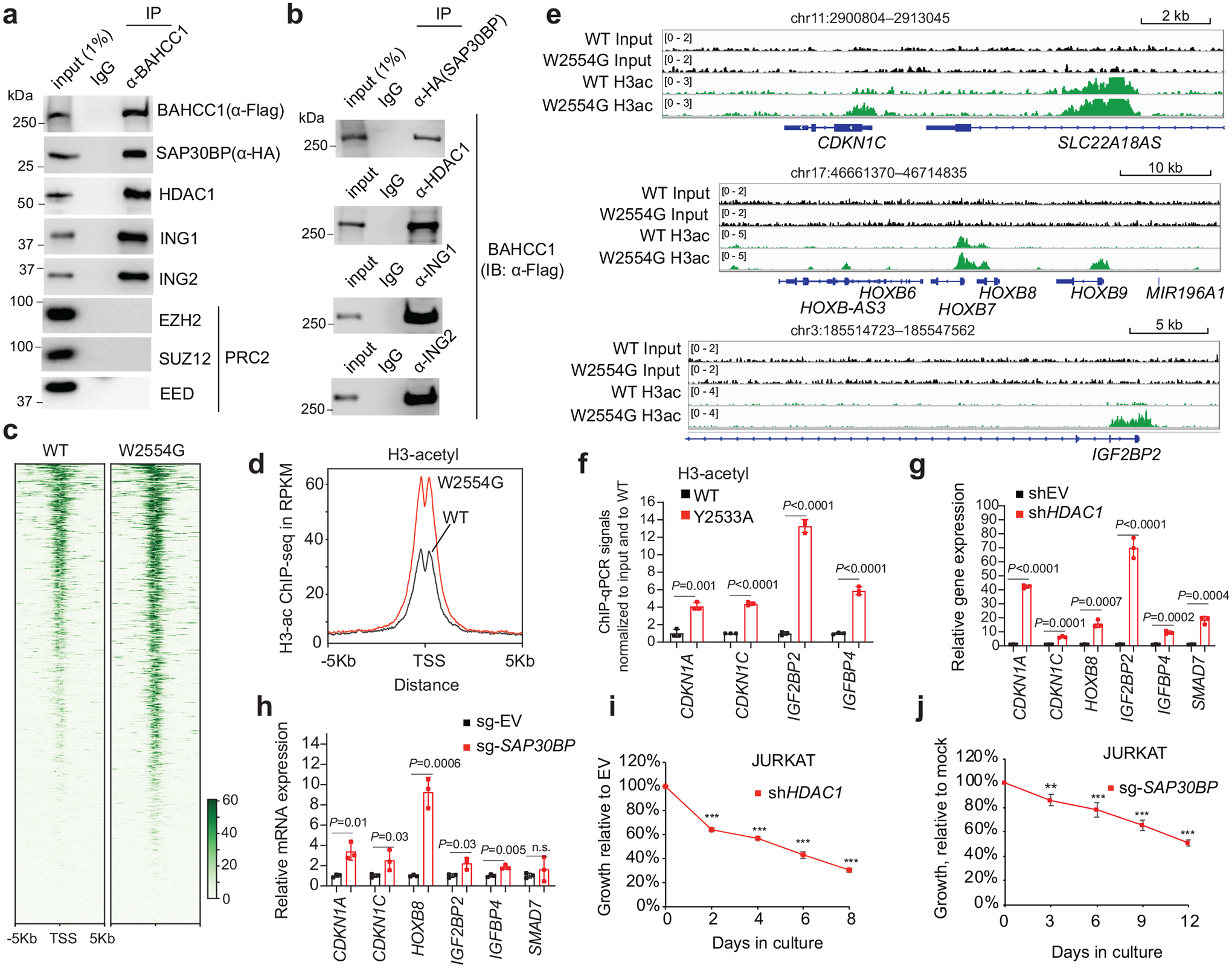
a-b, CoIP for interaction between endogenous Flag-BAHCC1 and the indicated HDAC1 or PRC2 complex component in JURKAT cells.
c-d, Heatmap (c) and averaged ChIP-seq signals (d) of histone acetylation across ±5 kb from TSS in JURKAT cells carrying either WT or the W2554G homozygous mutation of BAHCC1BAH.
e, ChIP-seq profiles of histone acetylation at the indicated gene in JURKAT cells harboring WT or the W2554G homozygous mutation of BAHCC1BAH.
f, ChIP-qPCR of histone acetylation at the indicated gene promoter in JURKAT cells that carry WT or the Y2533A homozygous mutation of BAHCC1BAH (n = 3 biologically independent samples). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
g-h, RT-qPCR of H3K27me3-marked genes post-depletion of HDAC1 (g) or SAP30BP (h) in JURKAT cells, compared to mock (n = 3 biologically independent samples). Data are presented as mean ± SD. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001.
i-j, Proliferation of JURKAT cells post-depletion of HDAC1 (i) or SAP30BP (j), compared to mock (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
