Fig. 7. BAHCC1 and PRC1 corepress the H3K27me3-marked genes in cells of different lineage origin.
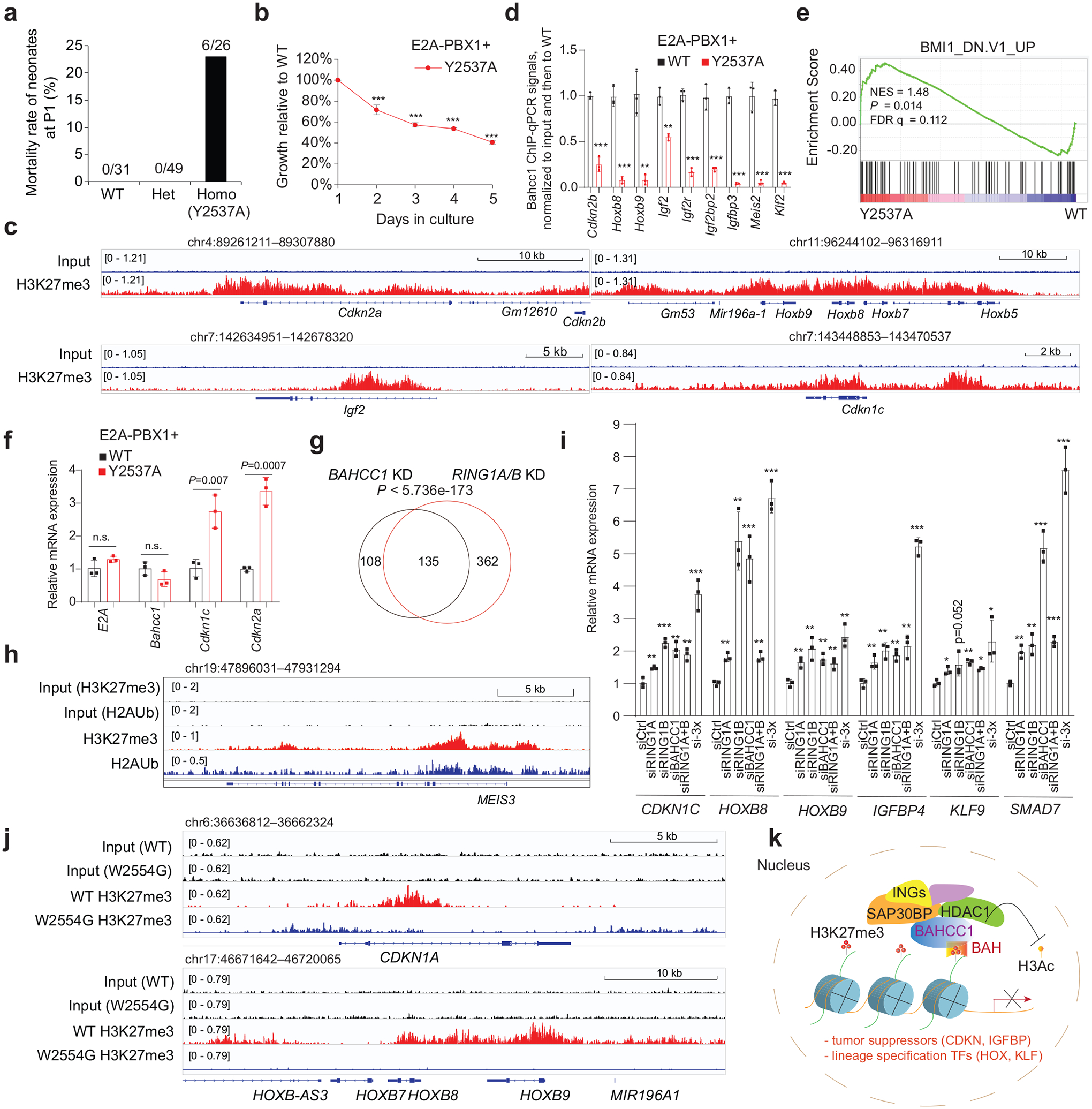
a, Mortality of mouse pups carrying either WT or the Y2537A heterozygous or homozygous mutation of Bahcc1, at day 1 post-birth (P1).
b, Proliferation of E2A-PBX1-transformed murine leukemia with the Y2537A homozygous mutation of Bahcc1BAH, relative to WT (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *** P < 0.001
c, H3K27me3 ChIP-seq profiles at classic Polycomb targets in E2A-PBX1-transformed murine leukemia cells.
d, ChIP-qPCR for Bahcc1 binding to TSS of the indicated gene in E2A-PBX1-transformed murine leukemia cells with WT or the Y2537A homozygous mutation of Bahcc1BAH (n = 3 independent experiments, with data plotted as mean ± SD after normalization to input and to WT). ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
e, GSEA reveals that, relative to WT, the H3K27me3-binding-defective mutation (Y2537A) of Bahcc1BAH is positively correlated to derepression of Polycomb genes.
f, RT-qPCR of E2A-PBX1, Bahcc1 and H3K27me3-targeted genes in E2A-PBX1-transformed murine leukemia cells with WT or the Y2537A homozygous mutations of Bahcc1BAH (n = 3 biologically independent samples). Data are presented as mean ± SD.
g, Venn diagram shows overlapping of DEGs upregulated post-depletion of BAHCC1 (black) or PRC1 (RING1A/1B; red), relative to mock, in 293 cells.
h, H3K27me3 and H2Aub ChIP-seq profiles at MEIS3, a classic Polycomb target, in 293 cells.
i, RT-qPCR of H3K27me3-targeted genes in 293 cells post-KD of RING1A, RING1B, BAHCC1, RING1A plus RING1B, or all three genes (si-3×), relative to mock (siCtrl). n = 3 biologically independent samples. Data are presented as mean ± SD. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
j, H3K27me3 ChIP-seq profiles at Polycomb targets in JURKAT cells with WT or the W2554G homozygous mutation of BAHCC1BAH.
k, Scheme showing that a previously unappreciated H3K27me3-transduction pathway, which functions through an H3K27me3-specific ‘reader’ module of BAHCC1BAH and BAHCC1-associated corepressors, exists in mammals for silencing the H3K27me3-bound targets, implicative of a new mechanism underlying the H3K27me3 readout. Of equal importance, such a process is crucially involved in oncogenesis.
