Extended Data Fig. 11|. Validation of ALPL inhibitor treatment and relevance to the human vasculature and Alzheimer’s disease.
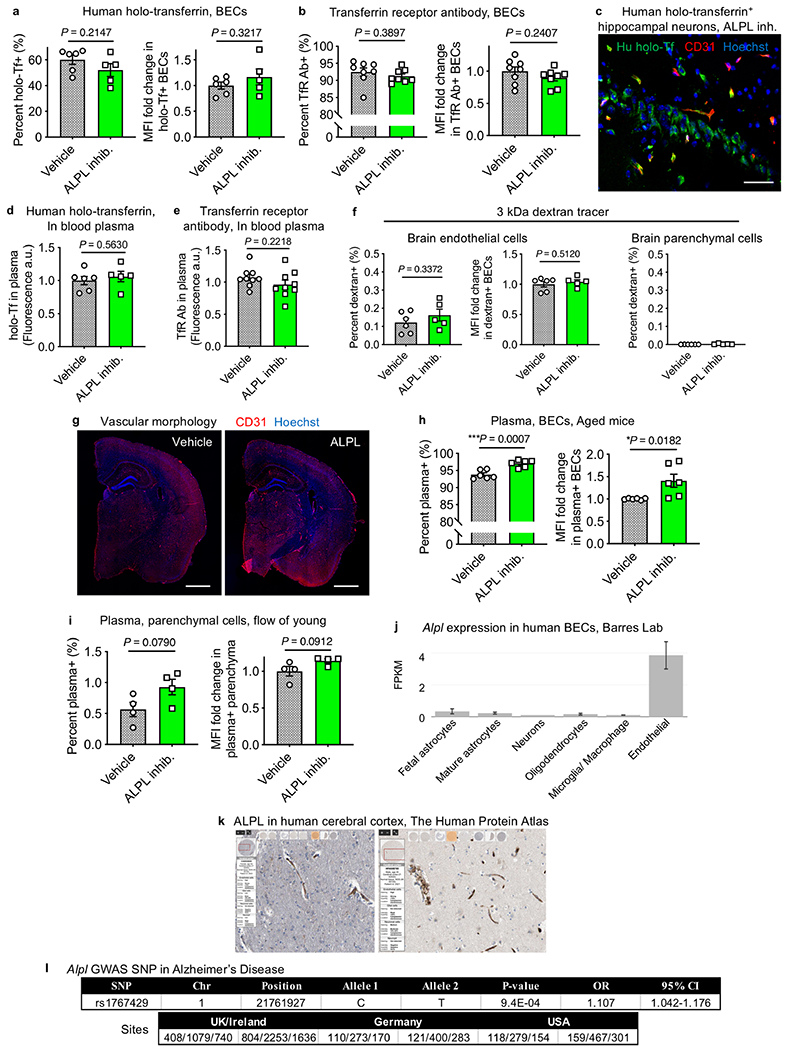
a, b, Flow cytometry quantification of BEC uptake of human holo-transferrin (hu-Tf) from aged (a) or TfR Ab from aged (b) mice treated with vehicle (grey) or ALPL inhibitor (green) via IP injections twice daily for 3 days, as assessed by the percent of BECs that are tracer+ and the relative MFI of tracer+ BECs (for hu-Tf: n = 6 mice vehicle, n = 5 ALPL inhibitor; for TfR Ab: n = 8; two-sided t-test; mean ± s.e.m.). Tracer refers to hu-Tf or TfR Ab. c, Representative images of human holo-Tf+ neurons detected in the cortex of mice treated with ALPL inhibitor. Scale bar, 40 μm. d, e, Circulating human holo-Tf (d) and TfR Ab (e) in blood plasma upon time of death to control for and ensure no differences in the injected amount (for hu-Tf+: n = 6 mice vehicle, n = 5 ALPL inhibitor; for TfR Ab: n = 9; two-sided t-test; mean ± s.e.m.). f, As in a and b, but for the 3-kDa dextran tracer that probes for disruptions in paracellular permeability (n = 6 mice vehicle, n = 5 ALPL inhibitor; two-sided t-test; mean ± s.e.m.). g, Overall cerebrovascular morphology, as assayed by CD31 staining, from aged mice (22 mo) treated with vehicle or an ALPL inhibitor. Scale bars, 1,000 μm. h, i, As in a and b, but for plasma uptake in BECs from aged mice (22 mo, n = 6) (h) and parenchymal cells from young mice (3 mo, n = 4; two-sided t-test; mean ± s.e.m.) (i). j, Alpl gene expression in various cell types of the human CNS, showing exclusive expression in endothelial cells. Data from Barres lab RNA-seq (http://www.brainrnaseq.org; mean ± s.e.m.)89. k, ALPL protein expression localized to the human brain vasculature in The Human Protein Atlas (http://www.proteinatlas.org)90,91. l, The Alpl single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1767429 shows association with Alzheimer’s disease (over 160,000 individuals, genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis)92.
