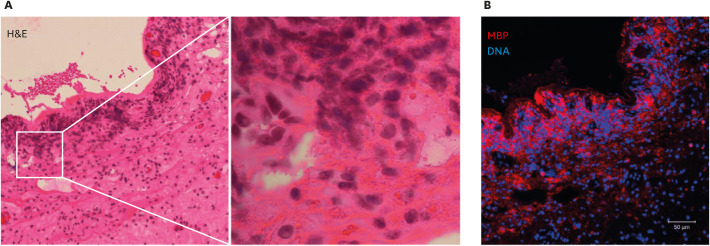
Fig. 3. Cytolytic eosinophils in a nasal polyp obtained from a case of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis).
(A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of a nasal polyp, showing a loss of epithelium and inflammatory cell infiltration in submucosal tissue. The boxed area in the left panel is shown magnified in the right panel. Accumulated cells showed cytolysis and a loss of nuclear shape (chromatolysis). Eosinophilic extracellular granules were also noted. (B) A serial section of the tissue shown in panel A was immunostained for major basic protein (MBP) (red) and counterstained for DNA (blue). Image was obtained with a Carl Zeiss LSM780 confocal microscope (×20). The massive deposition of extracellular MBP visible is consistent with the presence of cytolytic eosinophils.