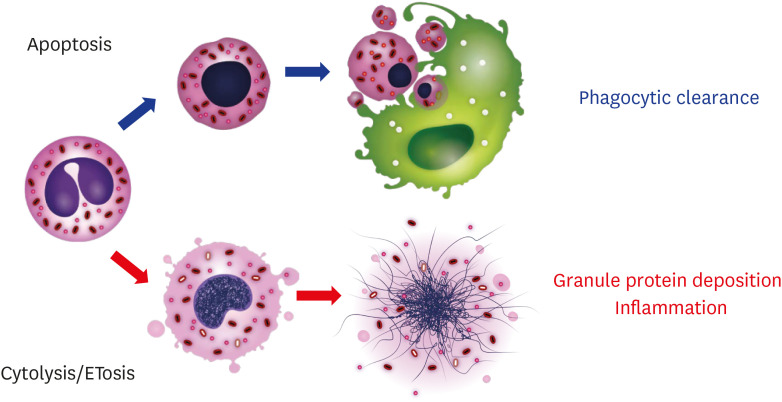
Fig. 4. Eosinophil cell fates and their consequences.
Eosinophils apoptosis can be caused by many factors, including aging, a loss of survival factors, corticosteroids, and anti-interleukin (IL)-5/anti-IL-5 receptor antibodies. Apoptotic eosinophils, typically with nuclear and cytoplasmic condensation, are phagocytosed without the induction of inflammation. Alternately, eosinophils can undergo ETosis upon activation, such as by an immunoglobulin-coated surface, pathogens, or platelet-activating factor with IL-5. Rapid cytolysis without the expression of a “find-me” signal results in the tissue deposition of the cell's total intracellular contents and prolonged inflammation.