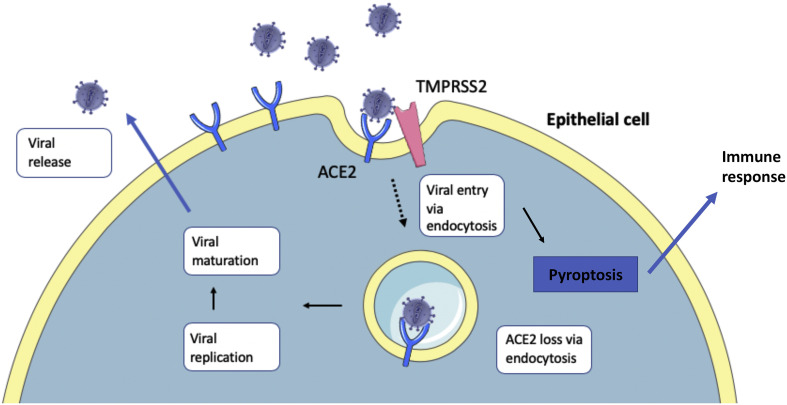
Fig. 1.
Epithelial entry of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 entry into respiratory epithelial cells is thought to be analogous to entry into cells of the central nervous system (CNS). After entering the airways, SARS-CoV-2 uses its spike (S) protein to bind the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on the cell surface of alveolar type II cells. Transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) primes the S protein to facilitate endocytosis of the bound ACE2 receptor [10]. The viral life cycle continues within the cell, culminating in viral replication and release after pyroptosis. The release of viral particles and cell death triggers downstream immune response cascades.