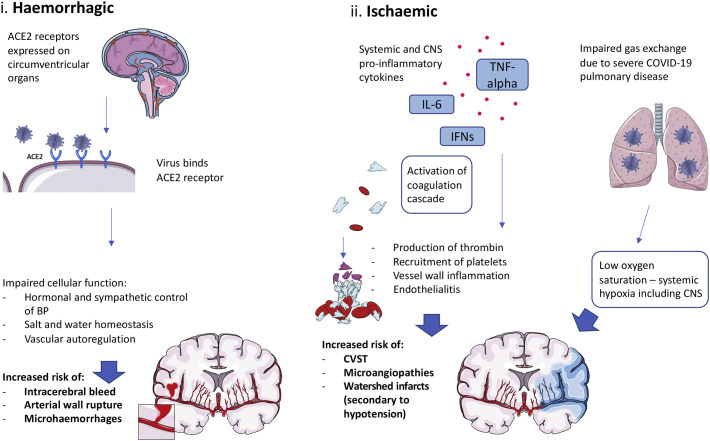
Fig. 4.
Mechanisms of vascular manifestations. Cerebrovascular manifestations can be separated into haemorrhagic and ischaemic diseases: i) Binding the ACE2 receptor on epithelial cells of the circumventricular organs leads to dysregulation of blood pressure homeostasis in the cerebral circulation, causing aneurysmal rupture and intracerebral bleeds [65]. ii) Impaired gas exchange due to COVID-19 effects on the respiratory system may result in poor oxygen delivery to the CNS. Cardiovascular compromise may also cause systemic hypotension and decreased perfusion to the CNS. Furthermore, circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines lead to activation of the coagulation cascade and vessel wall inflammation in the periphery and cerebrovasculature to increase the risk of various thrombotic complications [58].