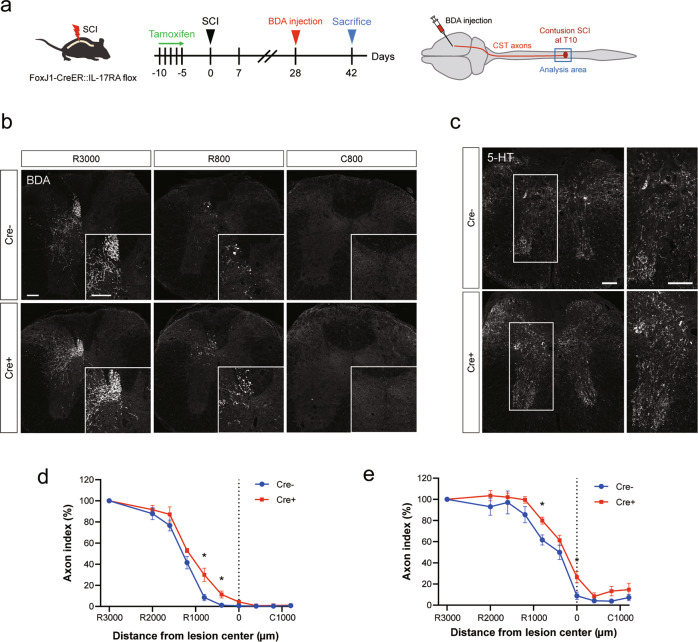
Fig. 4. Ependymal cell-specific inhibition of IL-17A signaling enhances axonal sprouting.
a Experimental time course of tamoxifen administration and BDA injection. b Representative images of BDA-labeled CST axons (white) in the transverse sections of the spinal cord at distances of 3000 µm rostral (R3000), 800 µm rostral (R800), and 800 µm caudal (C800) to the lesion epicenter. Upper: Control (Cre-) mouse. Lower: IL-17RA-deficient (Cre+) mouse. Scale bars: 100 μm. c Representative images of 5-HT-labeled axons (white) in the transverse sections of the spinal cord at 800 µm rostral to the lesion epicenter. Scale bars: 100 μm. d Quantification of the BDA-labeled CST axons at each site. The axon index (BDA-positive area) was increased in IL-17RA-deficient (Cre+) mice (n = 5, *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney U test). e Quantification of the 5-HT-labeled raphespinal tract axons at each site from the lesion epicenter. The axon index (5-HT-positive area) was increased in Cre+ mice (n = 5, *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney U test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.