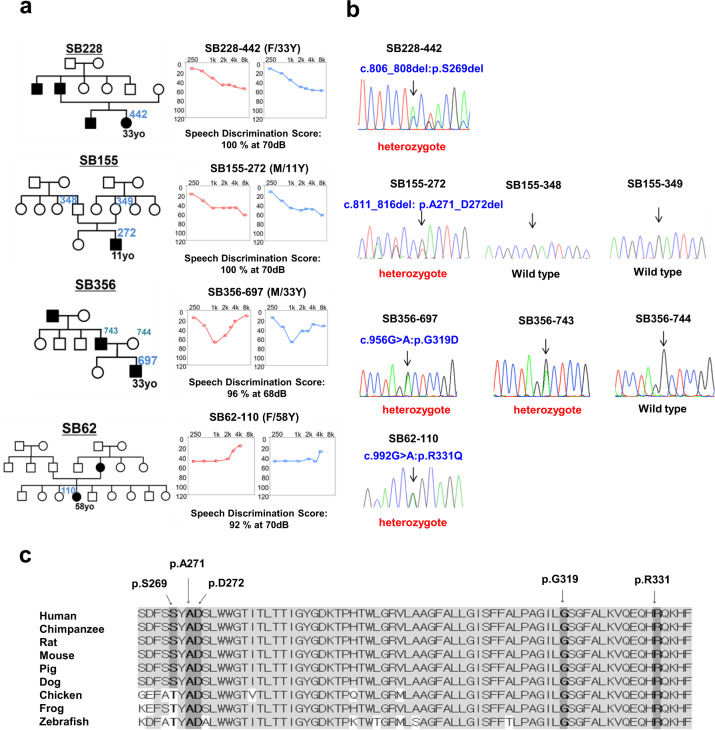
Fig. 1. Pedigree and audiological phenotypes and Sanger sequencing traces of novel KCNQ4 variants and the diverse topology of all reported KCNQ4 variants segregating with DFNA2.
a Pure-tone audiometry of the four probands with different audiological phenotypes: high-frequency (Families SB228 and SB155), mid-frequency (SB356), and low-frequency (SB62) sensorineural hearing loss. The upper horizontal axis shows tone frequency (Hz); the vertical axis indicates the hearing level (dB). We denote bone and air conduction pure-tone thresholds at different frequencies in the right (red color) and left (blue color) ears. b Pedigrees and Sanger sequence chromatograms. Three variants (p.A271_D272del (SB155), p.G319D (SB356), and p.R331Q of KCNQ4 (SB62)) are novel: a de novo, single heterozygous, in-frame deletion (SB155) and autosomal dominant, single heterozygous, missense variants of KCNQ4 (SB356 and SB62). c Well-conserved residues of three novel variants among various KCNQ4 orthologs.