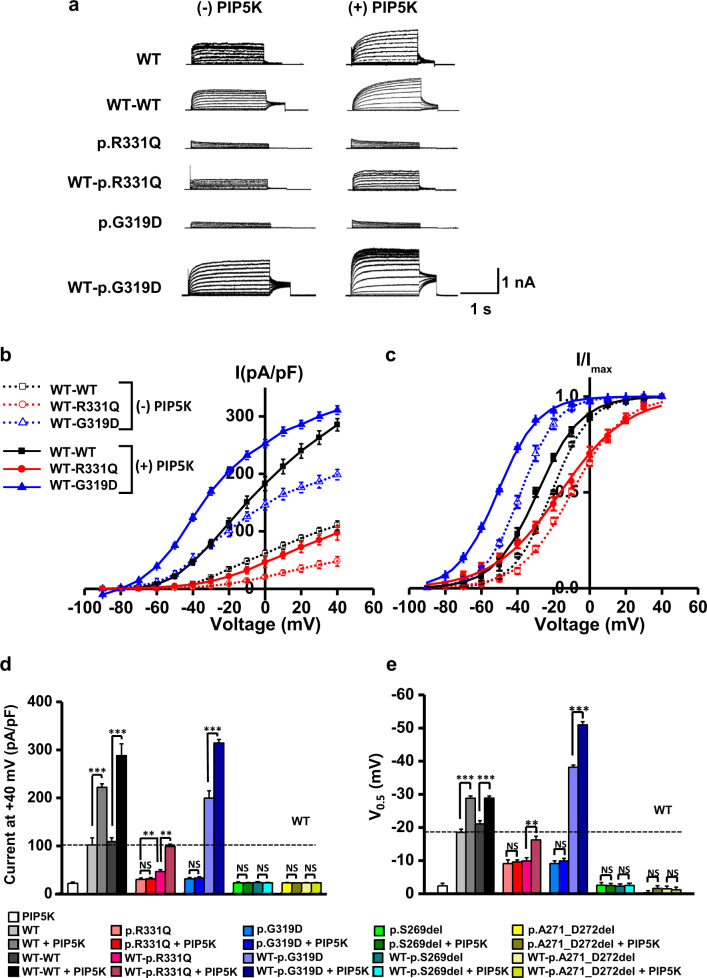
Fig. 3. Rescue effects of the PIP5 kinase on KCNQ4 mutant channels.
a The effects of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase (PIP5K) expression were compared between homomeric mutant channels (p.R331Q and p.G319D) and heteromeric tandem concatemer channels assembled from WT-p.R331Q and WT-p.G319D. Total K+ currents were measured in the absence (-PIP5K) or the presence of PIP5K expression (+PIP5K) in HEK293T cells. b Comparison of I-V curves between homomeric and tandem concatemer channels assembled from WT-WT, WT-p.R331Q, and WT-p.G319D. c Steady-state activation curves of the homomeric and tandem concatemer channels are compared (n = 10–12). d, e Comparison of K+ current densities measured at +40 mV and half-activation voltages (V0.5). WT-p.R331Q and WT-p.G319D concatemer mutant channels, but not homomeric mutant channels, were activated by PIP5K d, with a concomitant shifting of activation curve to negative voltage ranges e. Two pore-region mutant channels (p.S269del and p.A271_D272del) were unresponsive to PIP5K expression. The horizontal dotted lines in the graphs indicate the values obtained from homomeric WT channels (WT). The names of the groups are indicated in insets on the graph. Mean ± SEM (n = 10–12); **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005; NS, not significant.