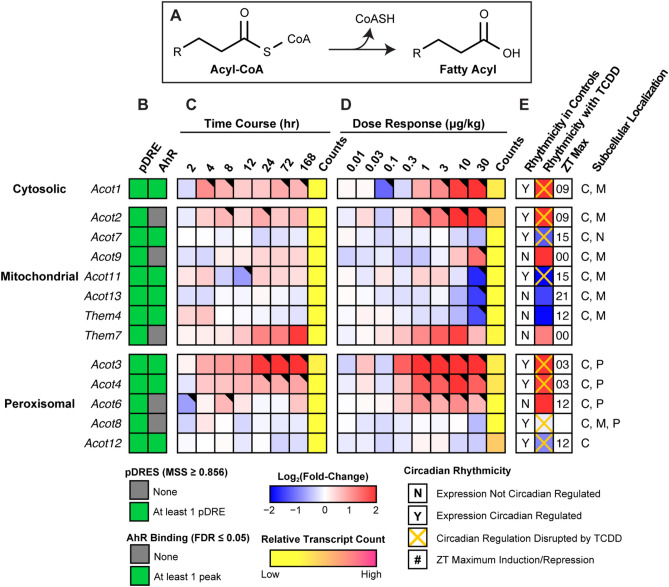
Figure 6.
Hydrolysis of acyl-CoAs. Differential expression of genes associated with fatty acid deactivation assessed by RNA-seq. (A) Fatty acid deactivation reaction catalyzed via acyl-CoA thioesterases. Official gene symbol designated in the MGI database are listed. (B) The presence of putative dioxin response elements (pDREs) and AHR enrichment at 2 h. (C) Time-dependent gene expression was assessed following a single bolus dose of 30 μg/kg TCDD (n = 3). (D) Dose-dependent gene expression following oral gavaged every 4 days for 28 days with 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 or 30 μg/kg TCDD (n = 3). (E) Circadian regulated genes are denoted with a “Y”. An orange ‘X’ indicates abolished diurnal rhythm following oral gavage with 30 μg/kg TCDD every 4 days for 28 days. ZT indicates statistically significant (P1(t) > 0.8) time of maximum gene induction/repression. Counts represents the maximum number of raw aligned reads for any treatment group. Low counts (< 500 reads) are denoted in yellow with high counts (> 10,000) in pink. Differential expression with a posterior probability (P1(t)) > 0.80 is indicated with a black triangle in the top right tile corner. Protein subcellular locations were obtained from COMPARTMENTS and abbreviated as: cytosol (C), mitochondrion (M), nucleus (N), and peroxisome (P). The heatmap was created using R (v4.0.4). The biochemical reaction was created using Adobe Illustrator (v25.2).