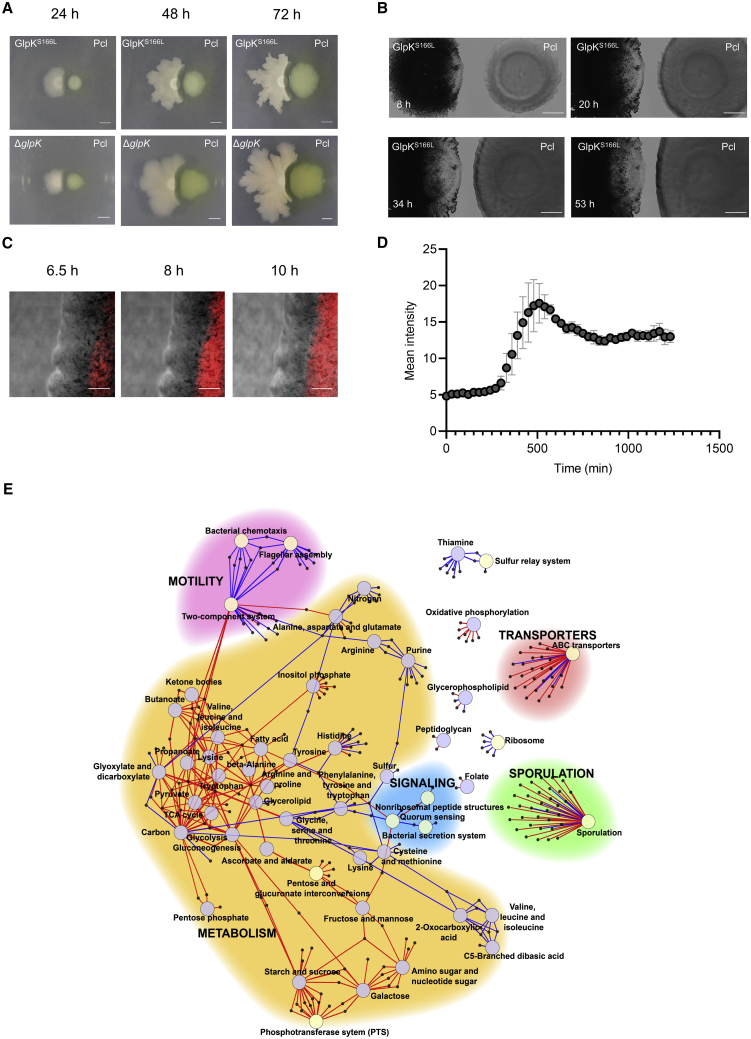
Figure 5.
Bamy glpK mutants suffer pleiotropic changes protecting from antibiosis of Pcl
(A) Time-course pairwise interactions between Pcl and GlpKS166L (top) and ΔglpK (bottom) at 24, 48, and 72 h. Scale bars, 5 mm.
(B) Time-lapse microscopy analysis of the pairwise interaction between Pcl and GlpKS166L during 48 h. Scale bars, 2 mm.
(C) CLSM time-course experiment of the interaction area between Pcl and GlpKS166L using PI (red fluorescence) to identify cell death of GlpKS166L. Images show the leading edge of the GlpKS166L colony. Scale bars, 40 μm.
(D) Measurement of PI fluorescence emitted by GlpKS166L during the interaction with Pcl as shown in (C). Error bars represent SD. n = 3.
(E) Differentially expressed genes between Bamy and GlpKS166L at 24 h clustered into different metabolic pathways. Larger circles indicate the main KEGG pathways, which are surrounded by arrows pointing to smaller circles that represent the differentially expressed genes. The color of the arrows indicates induction (red) or repression (blue). The color of the circles differentiates pathways involved in metabolism (light blue) from those not involved in metabolism (light yellow).