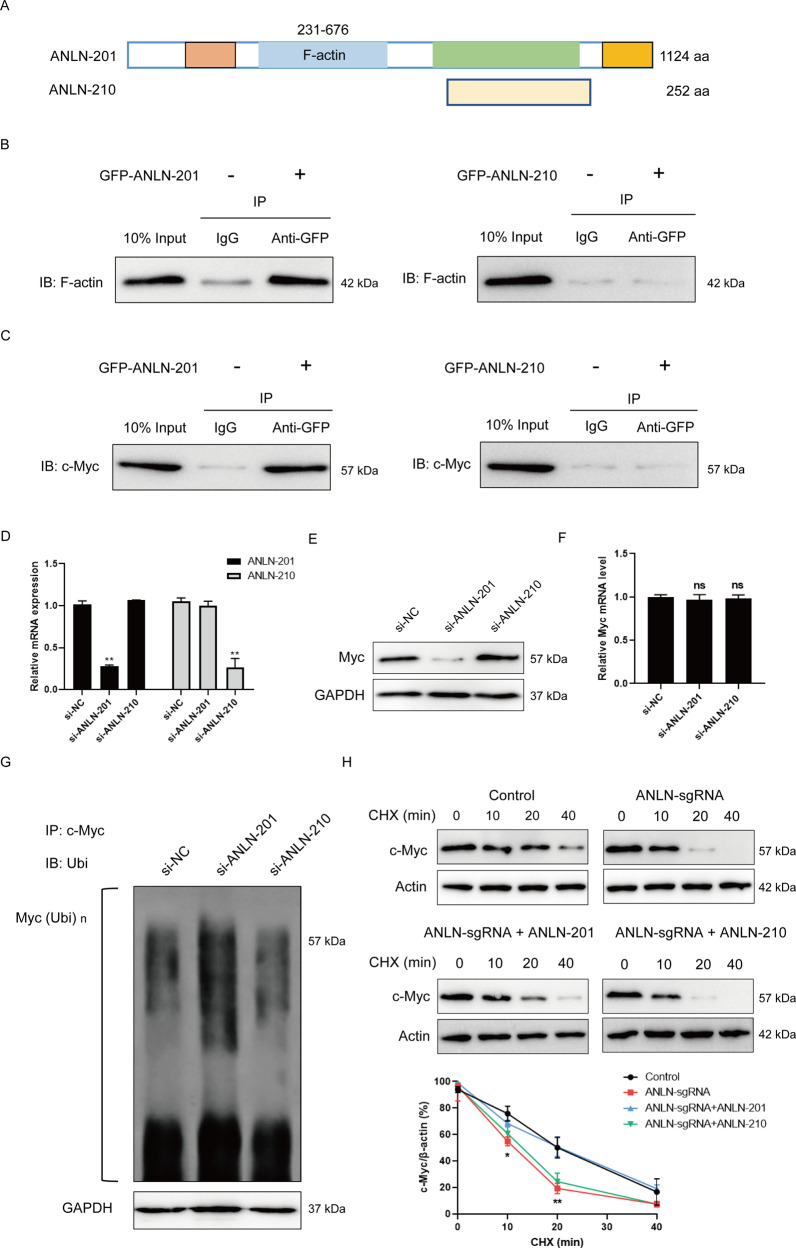
Fig. 3. ANLN-201 interacts with Myc.
A The sequence diagram of ANLN-201 and ANLN-210 was displayed. B SCC-9 cells were transfected with GFP-ANLN-201 or GFP-ANLN-210. Co-immunoprecipitation was performed between GFP-ANLN-201 or GFP-ANLN-210 and endogenous F-actin in SCC-9 cells using the <0.01. C Co-immunoprecipitation was performed between GFP-ANLN-210 or GFP-ANLN-201 and endogenous Myc in SCC-9 cells. D Transwell and transwell-matrigel assays were performed to measure cell migration and cell invasion caused by ANLN knockout. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. E Cell proliferation was assessed ed with si-ANLN-201 or si-ANLN-210. E The protein level of Myc was examined in si-ANLN-201 or si-ANLN-210 transfected SCC-9 cells. F The mRNA level of Myc was examined in si-ANLN-201 or si-ANLN-210 transfected SCC-9 cells. G Co-immunoprecipitation was performed in si-ANLN-201, si-ANLN-210, or si-NC transfected SCC-9 cells using antibody against Myc. Immunoprecipitates were subject to immunoblotting analysis using anti-ubiquitin. H SCC-9 cells were treated with 100 μM chlorhexidine (CHX) for 0, 10, 20, and 40 min in SCC-9 cells or ANLN-sgRNA SCC-9 cells transfected with GFP-control vector, GFP-ANLN-201 or GFP-ANLN-210. The protein level of Myc was detected by western blot. The relative level of Myc was determined by Image J. **P < 0.05, *P < 0.01.