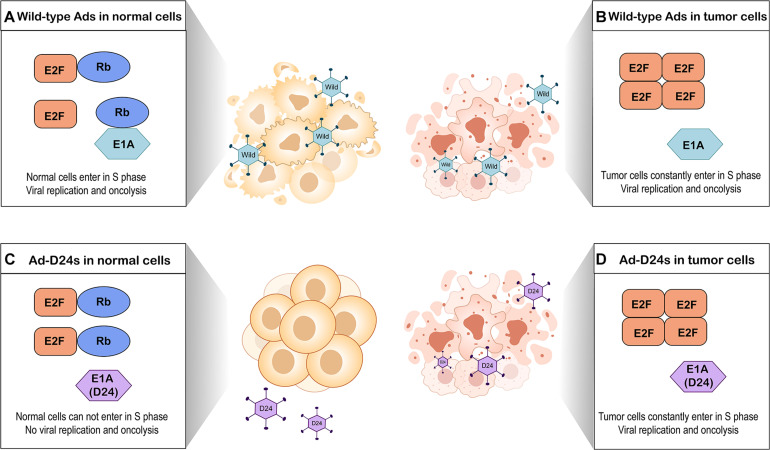
FIGURE 2.
Tumor selectivity of oncolytic adenoviruses with E1A gene 24-base pair deletion (Ad-D24s) and oncolytic adenoviruses without genomic modification (wild-type Ads). (A) Wild-type Ads infect normal cells. E1A protein of adenovirus interferes with Rb protein by binding it, leading to E2F release and accumulation. Free E2F allows the normal cells to enter into S phase of the cell cycle, which results in viral replication and oncolysis. (B) Wild-type Ads infect tumor cells. Due to the defective Rb pathway, the accumulation of free E2F allows tumor cells to constantly enter in S-phase. Wild-type Ads can replicate in the tumor cells and lyse them. (C) Ad-D24s infect normal cells but there is no viral replication and oncolysis. Mutated E1A protein cannot bind to Rb protein; therefore, E2F is still inactivated by Rb protein. The normal cells are unable to enter into S phase. (D) Tumor cells constantly enter in S-phase because of the defective Rb pathway; Ad-D24s can also lyse the tumor cells while generating viral progeny.