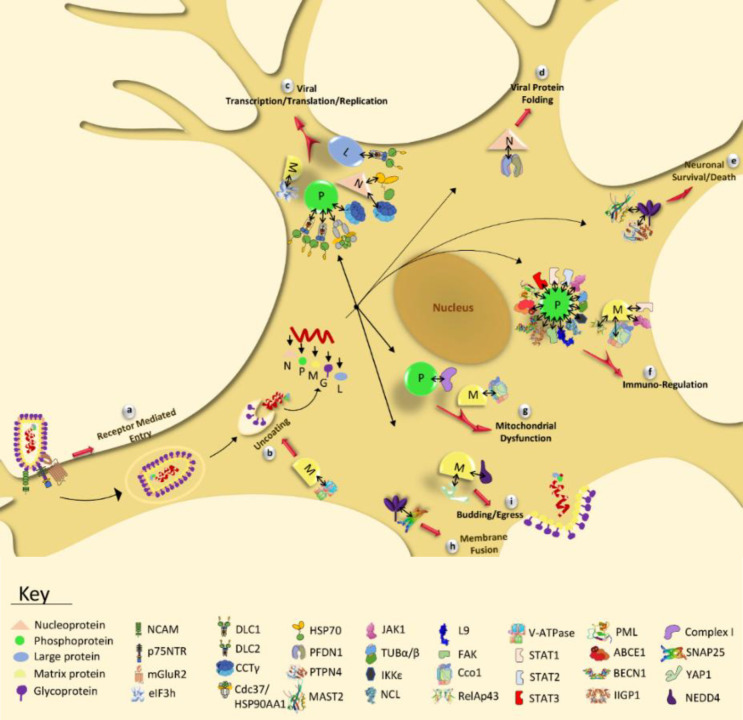
Fig. 7.
The lyssavirus-host experimentally defined PPIs and their functional/pathologic outcomes in rabies infection indicated in a neuron. G (glycoprotein), N (nucleoprotein), L (RNA-dependent polymerase or Large protein), P (phosphoprotein), and M (matrix protein) represent five viral proteins which interact with host proteins and facilitate receptor mediated entry of lyssavirus (a), uncoating (b), viral transcription/translation/replication (c), viral protein folding (d), neuronal survival/death (e), immuno-regulation (f), mitochondrial dysfunction (g), membrane fusion (h), and budding (i) during infection. Contribution of the identified PPIs in the mentioned processes has been displayed in the figure and explained in the text. The association of viral-host proteins is shown by right-leftwards arrows in black