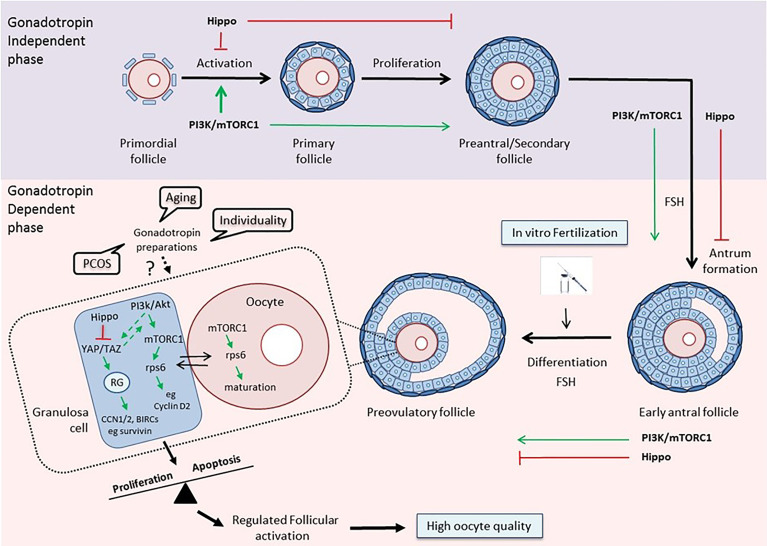
Figure 1.
The PI3K/mTOR/Hippo pathways as guidance for clinical decision-making. Top: The PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Hippo pathways exert opposite effects on follicular development during the gonadotropin-independent phase. Activation of the PI3K pathway is crucial for each growing stage of the follicle, especially at the primordial and primary stages (30, 94). The Hippo pathway acts in a coordinated manner with PI3K in order to accelerate primordial follicle activation and promote follicular development (48). Bottom: The two pathways maintain their concerted action on follicular development during the gonadotropin-dependent phase of follicular growth, and especially on the maturation of granulosa cells and oocytes in the preovulatory follicles, thereby assuring regulated follicular activation and high oocyte quality (79, 96). Various disease states, aging, and the uniqueness of each woman, by influencing this balance, may affect the response to different gonadotropin preparations, and consequently, the outcome of the IVF. The activation status of key components of the PI3K and Hippo pathways may serve as a prognostic or predictive biomarker that can help clinicians guide treatment planning. (RG, Regulatory Genes).