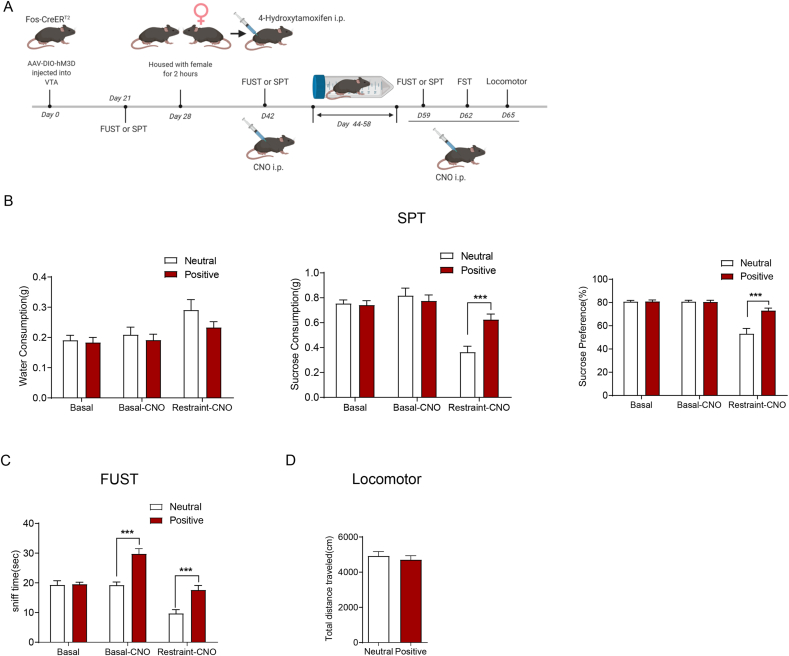
Fig. 3.
Acute reactivation of VTA neurons activated by positive experience ameliorates reward insensitivity induced by chronic restraint stress.
(A) The experimental timeline. (B) Sucrose preference test showing reactivation of hm3D-labell
ed VTA neurons during previous positive experience by CNO increased sucrose preference under chronic stress condition. Left, water consumption (subgroups, F (1, 21) = 1.586, P = 0.2218; treatment, F (2, 42) = 8.260, P = 0.0009; subgroups X treatment, F (2, 42) = 0.9042, P = 0.4126; Neutral VS. Positive, Basal P = 0.9932, Basal-CNO P = 0.9273, Restraint-CNO P = 0.2026); Middle, sucrose consumption (subgroups, F (1, 21) = 4.910, P = 0.0379; treatment, F (2, 42) = 22.72, P < 0.001; subgroups X treatment, F (2, 42) = 6.066, P = 0.0048; Neutral VS. Positive, Basal P = 0.9959, Basal-CNO P = 0.8748, Restraint-CNO P = 0.0004); Right, sucrose preference (subgroups, F (1, 21) = 10.09, P = 0.0046; treatment, F (2, 42) = 50.15, P < 0.001; subgroups X treatment, F (2, 42) = 14.20, P < 0.001; Neutral VS. Positive, Basal P = 0.9990, Basal-CNO P = 0.9998, Restraint-CNO P < 0.0001). (C) FUST showing reactivation of hm3D-labelled VTA neurons during previous positive experience by CNO increased sniff time under chronic stress condition (subgroups, F (1, 21) = 37.54, P < 0.001; treatment, F (2,42) = 32.22, P < 0.001; subgroups X treatment, F (2, 42) = 7.818, P = 0.0013; Neutral VS. Positive, Basal P = 0.9989, Basal-CNO P < 0.0001, Restraint-CNO P = 0.0002). (D) There was no significant difference in locomotor activity between two groups (two-tailed unpaired t-test, t(21) = 0.6287, P = 0.5364) under chronic stress condition. Neutral experience group n = 11, positive experience group n = 12 in SPT (B), FUST (C), FST (D) and locomotor (E). ***P < 0.001. Data are presented as means±SEM.