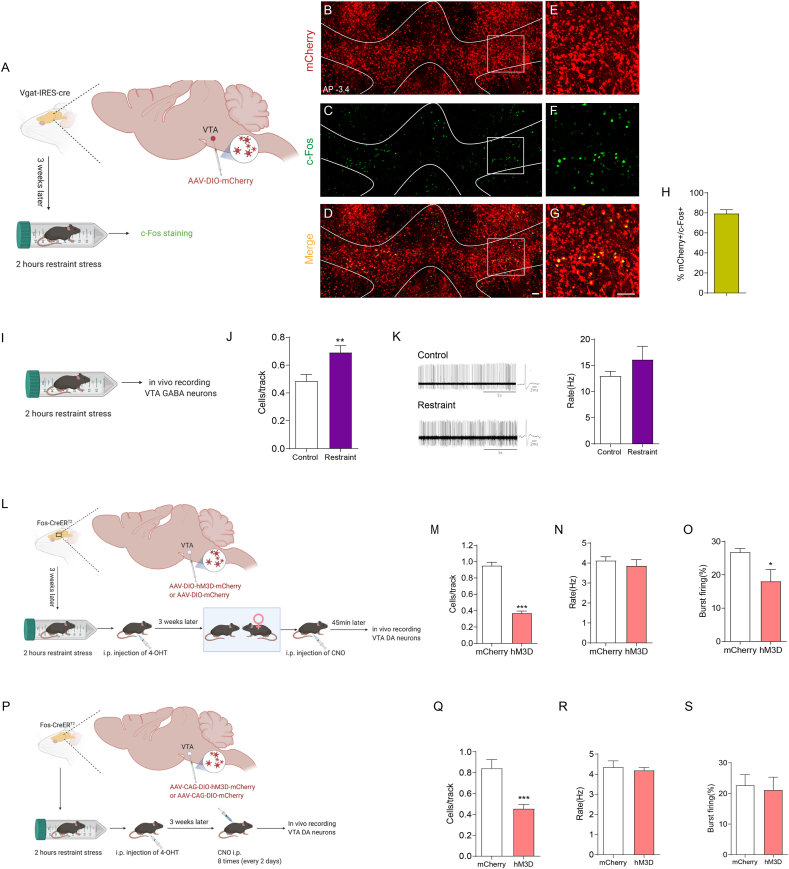
Fig. 6.
The VTA GABAergic neurons activated by restraint stress inhibit local VTA dopaminergic neurons responding to positive experience.
(A) Diagram illustrating virus injection in target areas and subsequent experiments. Representative images showing the expression of mCherry (B, E) and c-Fos staining (C, F) in VTA. (D, G) Images are merged. (H) Statistical analysis showing the percentage of mCherry -labelled VTA neurons positive also for c-Fos (79.49 ± 3.652 %, n = 5). (I) Schematic showing the experimental procedure for C57BL/6 J mice subject to restraint stress and subsequent in vivo extracellular recording. (J) Restraint stress increased the number of spontaneously active GABAergic neurons per track in the VTA (Mann-Whitney U test, P = 0.0089; C ontrol n = 8 mice (35 neurons), Restraint n = 9 mice (56 neurons)). (K) Left, representative extracellular voltage traces from VTA GABAergic neurons; Right, statistical result showing the average firing rate of the active GABAergic neurons (two-tailed unpaired t-test with Welch's correction, t(9.995) = 1.173, P = 0.2679; Control n = 8 mice (35 neurons), Restraint n = 9 mice (56 neurons)). (L) Diagram illustrating virus injection in target areas and subsequent experiments. Reactivation of VTA neurons previously activated by restraint stress inhibited the responsiveness of VTA dopaminergic neurons to sexual reward, decreasing the number of spontaneously active dopaminergic neurons per track in the VTA (M, Mann-Whitney U test, P < 0.0001; mCherry n = 7 mice (60 neurons), hM3D n = 9 mice (30 neurons)) and the percentage of burst firing (O, two-tailed unpaired t-test with Welch's correction, t(9.443) = 2.370, P = 0.0406; mCherry n = 7 mice (60 neurons), hM3D n = 9 mice (30 neurons)), but no change in the firing rate (N, two-tailed unpaired t-test, t(14) = 0.6785,P = 0.5085; mCherry n = 7 (60 neurons), hM3D n = 9 mice (30 neurons)). (P) Diagram illustrating virus injection in target areas and subsequent experiments. Chronic reactivation of VTA neurons previously activated by restraint stress decreased the number of spontaneously active dopaminergic neurons per track in the VTA (Q, Mann-Whitney U test, P = 0.0002; mCherry n = 9 mice (67 neurons), hM3D n = 10 mice (42 neurons)), but no change in the firing rate (R, two-tailed unpaired t-test, t(17) = 0.2940, P = 0.7723; mCherry n = 9 (67 neurons), hM3D n = 10 mice (42 neurons)) and the percentage of burst firing (S, two-tailed unpaired t-test, t(17) = 0.5666, P = 0.5784; mCherry n = 9 (67 neurons), hM3D n = 10 mice (42 neurons)), under normal condition. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are presented as means±SEM. Annotation (AP): distance from the bregma (mm). Scale bars correspond to 100 μm.