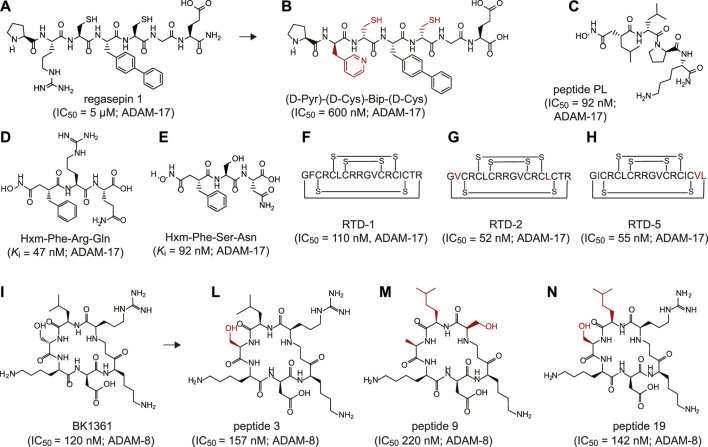
FIGURE 1.
Peptide inhibitors of ADAM proteins. (A) Chemical structure of regasepin 1 linear peptide (PRC(Bip)CGE); (B) Chemical structure of regasepin 1-derived linear peptide (D-Pyr)-(D-Cys)-Bip-(D-Cys); (C) Chemical structure of peptide PL (Hisb-LPK-NH2); (D) Chemical structure of linear peptide Hxm-FRQ; (E) Chemical structure of linear peptide Hxm-FSN; (F) Schematically depicted structure of polycyclic octadecapeptide rhesus θ-defensin-1 (RTD-1) peptide; (G) Schematically depicted structure of polycyclic octadecapeptide rhesus θ-defensin-2 (RTD-2) peptide; (H) Schematically depicted structure of polycyclic octadecapeptide rhesus θ-defensin-5 (RTD-5) peptide; (I) Chemical structure of cyclic peptide BK1361 (RLsKDK); (L) Chemical structure of cyclic peptide 3 (RLhSβKDK); (M) Chemical structure of cyclic peptide 9 (RL*AβKDK); (N) Chemical structure of cyclic peptide 19 (RL*hSβKDK). Indicated half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and inhibition constant (Ki) values were reported as published. The targeted ADAM protein is reported near the IC50 or K i value. Legend: Bip = biphenylalanine, Pyr = pyridylalanine, Hisb = (R)-2-isobutylsuccin hydroxamate moiety, Hmx = hydroxamate moiety, s = D-serine; hSβ = β-homoserine, Aβ = β-alanine, L* = homoleucine. The side chains that differentiate from the parental peptide are shown in red.