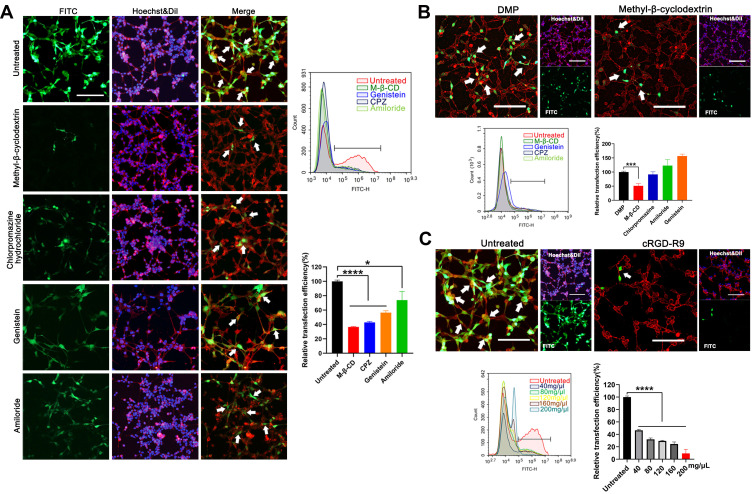
Figure 3.
Study on the cellular uptake mechanism of the DMP-039/mRNA complex. (A) Fluorescent images of internalization of the DMP-039/mRNA complex after being treated with various inhibitors; the uptake rates were calculated by flow cytometry (scale bar: 100 μm) (*P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001). Representative EGFP mRNA signals are marked by white arrows. (B) The internalization of the DMP/mRNA complex was found to be suppressed only by methyl-β-cyclodextrin, as determined by fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry (scale bar: 100 μm) (***P < 0.001). Representative EGFP mRNA signals are marked by white arrows. (C) The internalization of the DMP-039/mRNA complex was obviously suppressed by cRGD-R9 (200 mg/μL), as determined by fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry (scale bar: 100 μm) (****P < 0.0001). Representative EGFP mRNA signals are marked by white arrows. All cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue), and plasma membranes were stained with Dil (red) (scale bar: 100 μm).