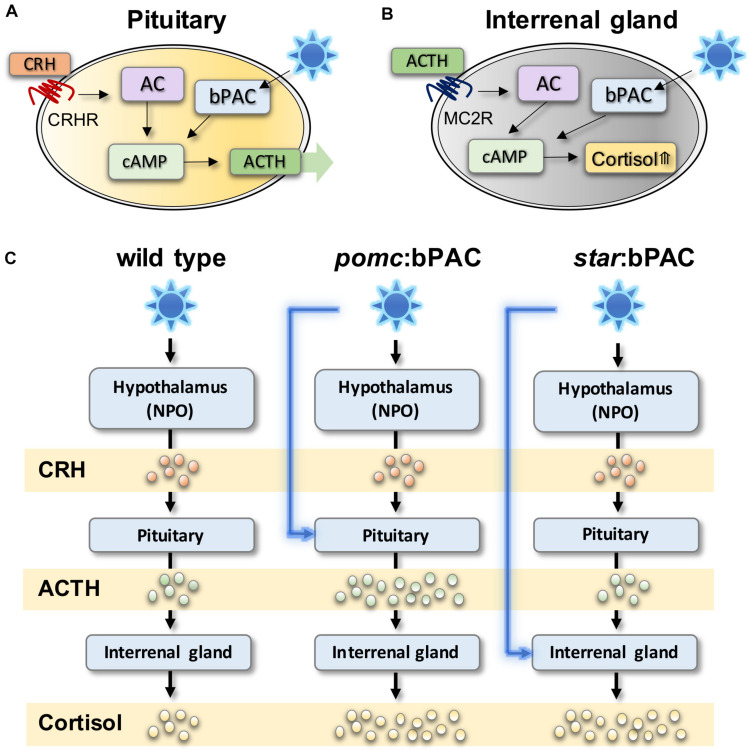
FIGURE 1.
Optogenetic modulation of stress hormones in zebrafish can be used to study acute and long-term effects of HPI axis modulation. (A) In pituitary corticotroph cells, bPAC activation via blue light exposure activates cAMP signalling, which is expected to amplify ACTH release from the pituitary. (B) In steroidogenic cells bPAC activation by blue light activates cAMP signalling which leads to increased level of cortisol. (C) In transgenic pomc:bPAC larvae, exposure to blue light leads to hyperactivation of the HPI axis at the level of the pituitary, and also the interrenal gland, since increased bPAC-induced ACTH release drives increased cortisol release, meanwhile targeting bPAC to steroidogenic cells of the interrenal gland in star:bPAC larvae leads to overproduction of cortisol only, under blue light exposure. Adapted from Gutierrez-Triana et al. (2015), De Marco et al. (2016).