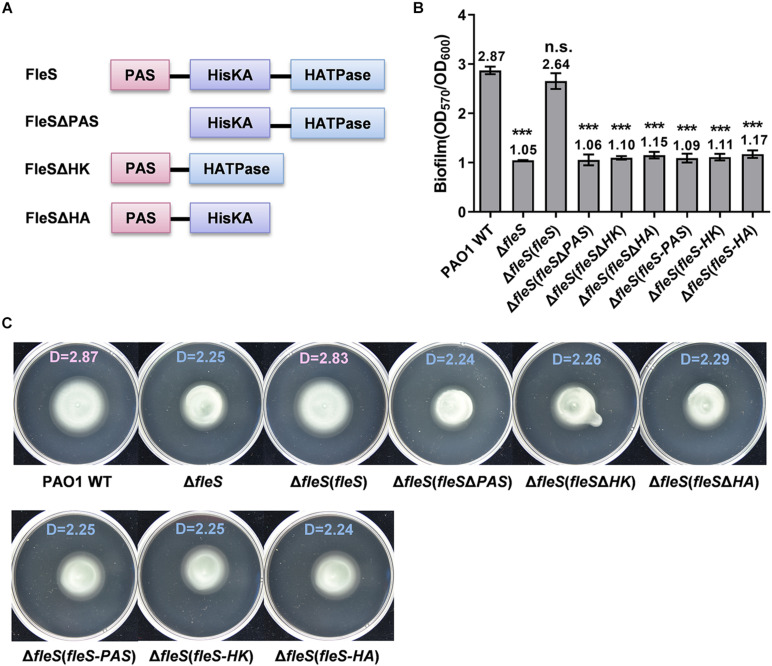
FIGURE 1.
PAS, HisKA, and HATPase domains in FleS are all essential for its signaling to regulate biofilm formation and swimming motility. (A) A schematic diagram showing the domain structures of FleS and its variants. Domain structures were predicted using the SMART program (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). (B) Biofilm formation of the PAO1 wild type (WT), the ?fleS mutant and the ?fleS mutant with ectopic expression of FleS, FleSΔPAS, FleSΔHK, FleSΔHA as well as the single FleS domains FleS-PAS, FleS-HK, and FleS-HA. The result is shown as the mean of five replicates per strain and error bar indicates the standard error of mean (SEM). ***P < 0.001, n.s., no significance (Student’s t-test). (C) Swimming motility of the PAO1 wild type, the ΔfleS mutant and the ΔfleS mutant with ectopic expression of FleS, FleSΔPAS, FleSΔHK, FleSΔHA, FleS-PAS, FleS-HK, and FleS-HA. Representative images and the average diameter (D) of the swimming migration zone of each strain are shown. Each experiment was performed in triplicate.