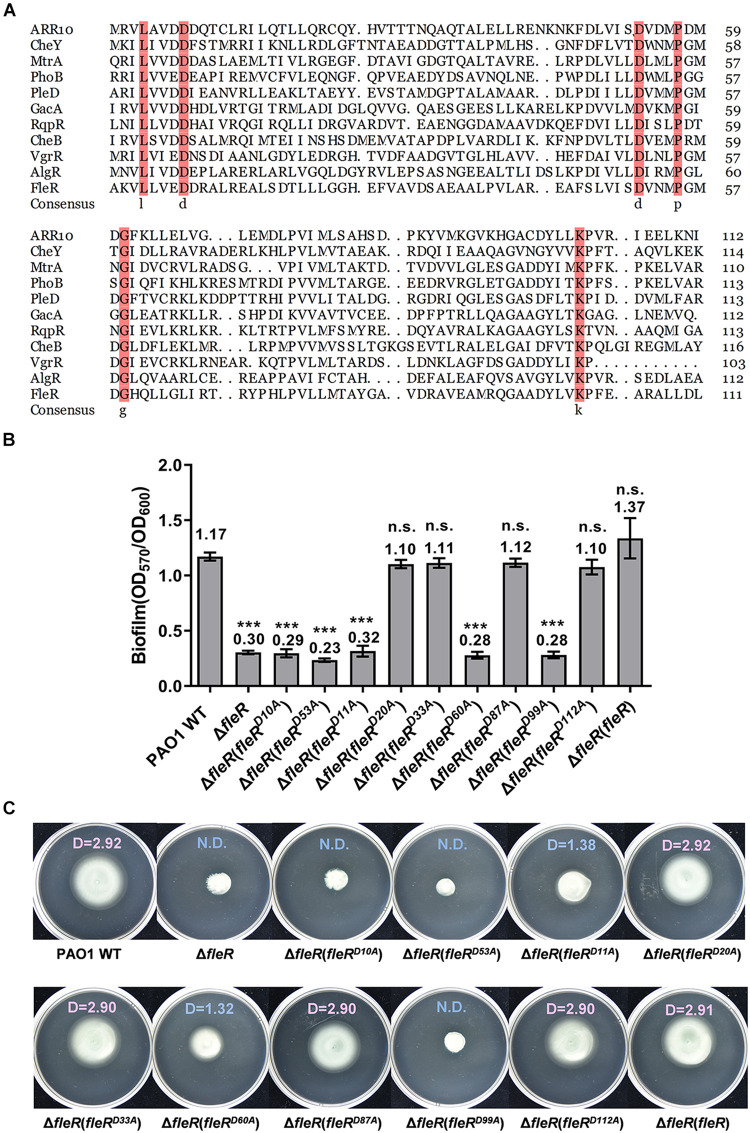
FIGURE 4.
Aspartate residues at positions of 10, 11, 53, 60, 99 in the REC domain of FleR are essential for the FleR activity. (A) Sequence alignment of the REC domain of FleR with 10 canonical REC domain sequences from ARR10 (NP_194920.1), CheB (WP_001350517.1), NreC (CPM47396.1), MtrA (AAB07804.1), PhoB (WP_000113933.1), PleD (WP_004620047.1), VgrR (WP_003490678.1), GacA (AAA68948.1), AlgR (AAA88427.1), and RqpR (CDN61654.1). The arrows indicated the potential aspartate residue to receive phosphoryl group. (B,C) The role of all the aspartate residues in FleR REC in controlling biofilm formation (B) and swimming motility (C) was examined by ectopic expression of FleR containing each D to A substitution in the ΔfleR strain. ***P < 0.001, n.s., no significance (Student’s t-test). Representative images and the average diameter (D) of the swimming migration zone of each strain are shown. N.D., not detected. Each experiment was performed in triplicate.