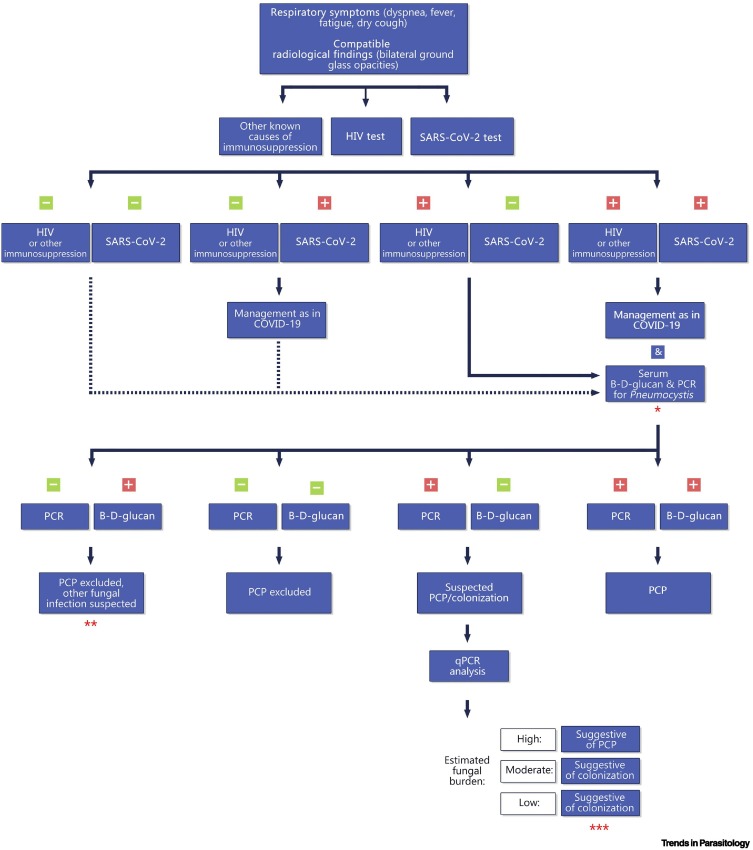
Figure 1.
Proposed diagnostic pathway for suspected SARS-CoV-2 and Pneumocystis jirovecii coinfection.
⁎Additional testing for P. jirovecii should be considered especially in less common risk groups (e.g., patients with mild immunosuppression) or those with SARS-CoV-2-related lymphopenia. ⁎⁎In view of various factors associated with the intensive care unit (ICU) setting (e.g., host proinflammatory responses, drug administration, blood transfusion, or application of blood products), consider false-positive (1,3)-β-d-glucan (BDG) results. ⁎⁎⁎Of note, P. jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in non-HIV-infected immunocompromised individuals may be associated with low and moderate fungal burdens; also, false-negative BDG results (e.g., due to treatment with antifungal agents) may be considered. Abbreviations: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; qPCR, quantitative PCR; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.