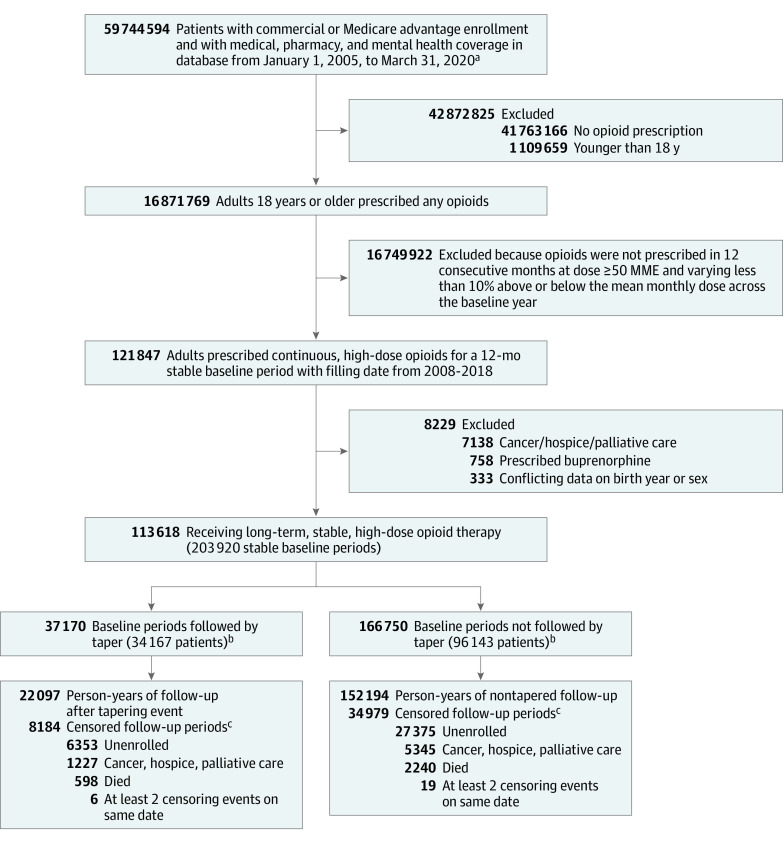
Figure 1. Selection and Inclusion of Patients in a Study of the Association of Dose Tapering With Overdose or Mental Health Crisis Among Patients Prescribed Long-term Opioids.
aInitial date range chosen to allow adequate buffering on either end of study period (January 1, 2007, through December 31, 2019).
bA total of 34 167 patients had at least 1 baseline period followed by a taper event, of whom 29 101 had a tapering event following their most recent stable baseline period. Similarly, 96 143 patients contributed a baseline period that was not followed by a tapering event, of whom 84 517 patients did not undergo tapering following their most recent stable baseline period, as reflected in Table 1. In analyses, patients who underwent tapering contributed pretaper follow-up time to the nontapered group.
cCensoring events occurred in 8184 of 37 170 (22.0%) follow-up periods after tapering events and 34 979 of 166 750 (21.0%) follow-up periods when no tapering event was identified.