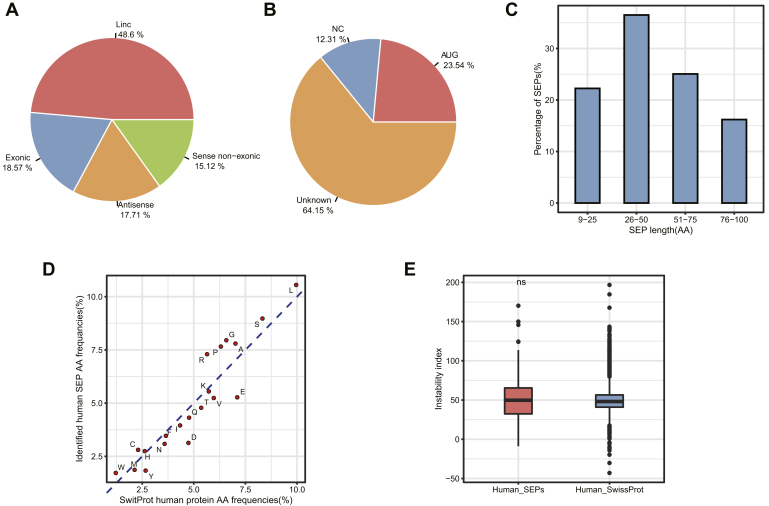
Fig. 5.
Characterization of the identified SEPs and their corresponding lncRNAs.A, classification of human SEP-coding lncRNAs based on their location on the genome with respect to protein-coding genes. B, usage of start codon in human SEPs. Nearly 77% of the identified lncRNA-SEPs were found to be initiated with non-AUG start codons. AUG, smORF initiates with AUG; NC, near cognate start codon, containing only one nucleotide different from AUG; unknown, smORF not initiated with AUG and not an NC. C, length distribution of human SEPs. D, the amino acid usage of canonical proteins and identified human SEPs. The human SEPs identified in this study tend to utilize more positively charged amino acids (such as K) and less negatively charged amino acids (such as D and E), while using a similar amount of uncharged amino acids, as observed in canonical proteins. E, stability of the identified human SEPs. The instability index was calculated by ProtParam and used to characterize the protein stability of human SEPs. There is only a minor deviation between the instability index distributions of the identified SEPs and canonical proteins. lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; SEP, small ORF-encoded polypeptide.