FIGURE 3.
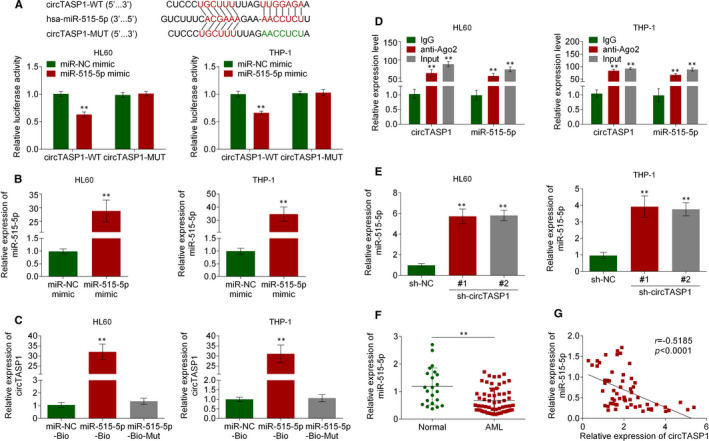
CircTASP1 functioned as a molecular sponge of miR‐515‐5p. A, The binding site of miR‐515‐5p and circTASP1 was predicted by circinteractome, and the interaction of miR‐515‐5p and circTASP1 was examined by luciferase activity assay. B, QRT‐PCR assay suggested that miR‐515‐5p mimic significantly increased miR‐515‐5p expression in HL60 and THP‐1 cells. C, RNA pull‐down assay was performed with miR‐515‐5p‐biotin, miR‐515‐5p‐biotin‐MUT or miR‐NC‐biotin using HL60 and THP‐1 cell extracts. RNA levels of circTASP1 in immunoprecipitates were detected by qRT‐PCR. D, RIP assay indicated that circTASP1 and miR‐515‐5p were specifically bound by AGO2. E, QRT‐PCR assay confirmed that knockdown of circTASP1 promoted miR‐515‐5p expression in HL60 and THP‐1 cells. F, The qTR‐PCR analysis of the relative expression of miR‐515‐5p in patients with AML and normal individuals. G, Pearson's correlation coefficients were used to evaluate the correlation between circTASP1 and miR‐515‐5p in patients with AML. **P < .01. Each experiment was repeated 3 times
