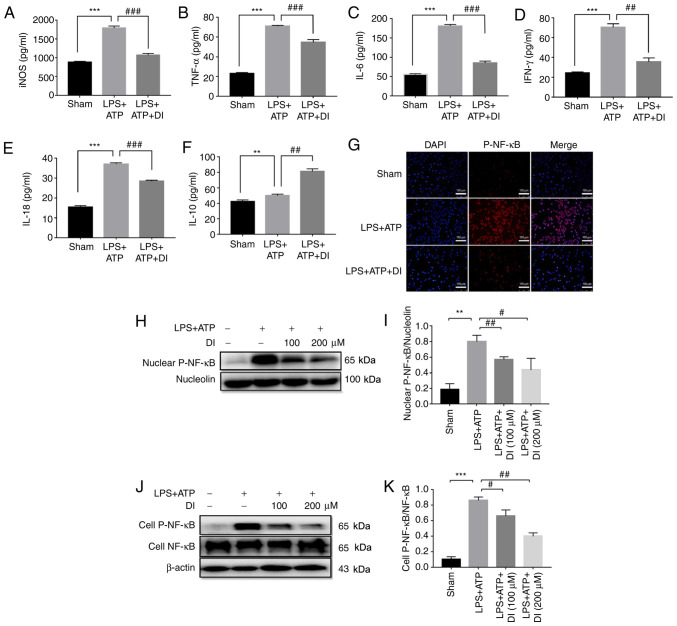
Figure 5.
DI regulates microglia inflammatory profile via inhibiting NF-κB phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Levels of cytokines, including (A) iNOS, (B) TNF-α, (C) IL-6, (D) IFN-γ, (E) IL-18 and (F) IL-10, were determined by ELISA. (G) Nuclear translocation of p-NF-κB was determined by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar, 100 µm. (H and I) p-NF-κB expression in the nucleus were determined by western blotting. (J and K) Ratio of whole cell p-NF-κB/total NF-κB expression was determined by western blotting. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n=3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs. LPS+ATP group. DI, dimethyl itaconate; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; p-, phosphorylated.