Figure 1: High-power, Short-duration Radiofrequency Compared with Standard Radiofrequency Ablation.
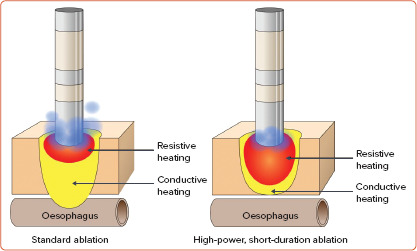
Longer applications using conventional parameters (20.30 W for 20.40 seconds) result in more conductive heating that reaches deep structures (left). The presumed advantage of higher powers with shorter durations (≥50 W for 5.12 seconds) is the larger endocardial lesion as a result of the high energy applied from the tip of the catheter to the myocardium (resistive heating) but less conduction of heat to deeper structures (right). Higher irrigation used in conventional ablation also translates into deeper lesions (left). Conversely, lower irrigation only creates superficial and non-transmural lesions (right).
