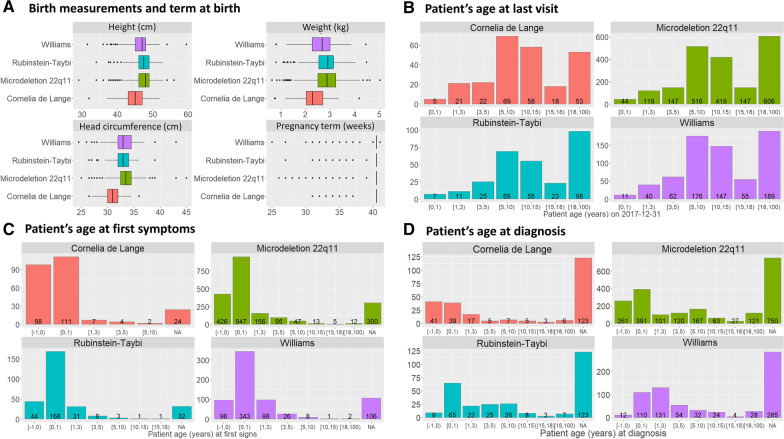
Fig. 3.
Focus on two chromosomal diseases (Williams (n = 681) and 22q11 microdeletion (n = 2,008) syndromes) and two monogenic diseases (Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (n = 290) and Cornelia de Lange syndrome (n = 246)) as examples. A Birth measurements and term at birth. For each measurement by disease, number of patients. Cornelia de Lange syndrome: birth height (n = 99), birth weight (n = 110), head circumference (n = 97), term at birth (n = 252). 22q11 microdeletion syndrome: birth height (n = 764), birth weight (n = 862), head circumference (n = 710), term at birth (n = 2,033). Rubinstein Taybi syndrome: birth height (n = 171), birth weight (n = 184), head circumference (n = 150), term at birth (n = 295). Williams syndrome: birth height (n = 317), birth weight (n = 352), head circumference (n = 291), term at birth (n = 680). B Patient’s age at last visit. For each disease, number of patients: Cornelia de Lange syndrome (n = 246), 22q11 microdeletion syndrome (n = 1,998), Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (n = 288), Williams syndrome (n = 680). C Patient’s age at first symptoms. For each disease, number of patients: Cornelia de Lange syndrome (n = 222), 22q11 microdeletion syndrome (n = 1,701), Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (n = 256), Williams syndrome (n = 574). D Patients’ age at diagnosis. For each disease, number of patients: Cornelia de Lange syndrome (n = 123), 22q11 microdeletion syndrome (n = 1,251), Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (n = 165), Williams syndrome (n = 395). On all graphs, Williams syndrome is represented in purple, 22q11 microdeletion syndrome in green, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in blue and Cornelia de Lange syndrome in red