Figure 5.
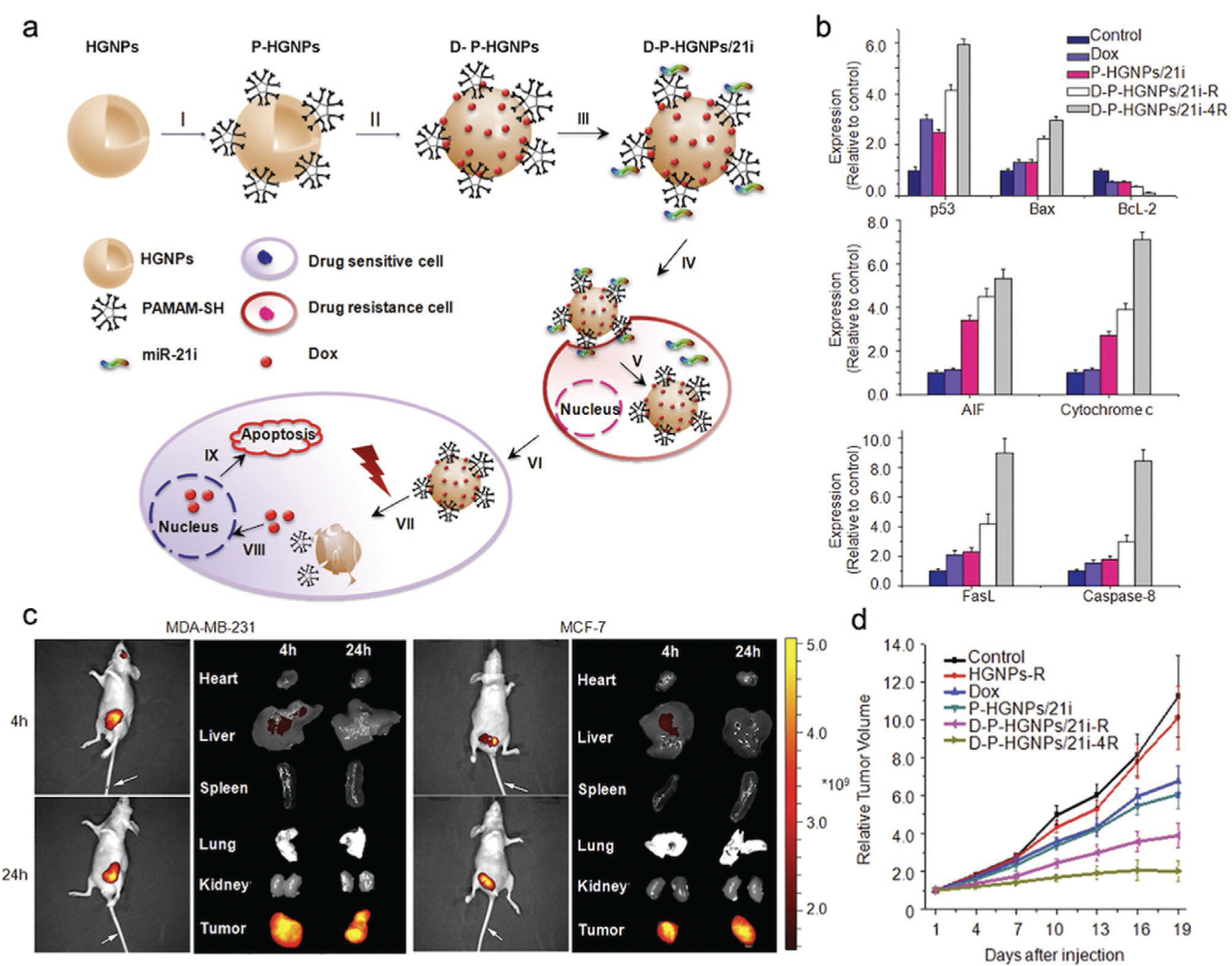
HGNPs with NIR release mechanism for co-delivery of Dox and miR-21i to breast tumors. a) Schematic illustration of HGNP-based, NIR triggered sequential miR-21i/Dox release with a precise time interval for optimal combination therapy. I–III) Formation of the HGNP co-delivery system. IV) D-P-HGNP/21i enters cells through endocytosis. V) Upon entering tumor cells, miR-21i is released first, VI) modulating the intrinsic state to a more chemosensitive state. VII) At the desired time, application of an NIR laser triggers collapse of HGNPs and a burst release of Dox, IX) activating two apoptosis signaling pathways, thereby inducing the synergistic apoptosis response. b) Quantitative results of western blotting indicate that both mitochondrial apoptosis and death receptor-related apoptosis pathways were activated by sequential therapy. c) Distribution of D-P-HGNP/21i in MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 tumor-bearing mice at 4 and 24 h postinjection with Cy5.5 labeled D-P-HGNP/21i. d) Tumor growth curves for nude mice bearing MDA-MB-231 human breast tumors. Reproduced with permission.[146] Copyright 2016, Elsevier.
