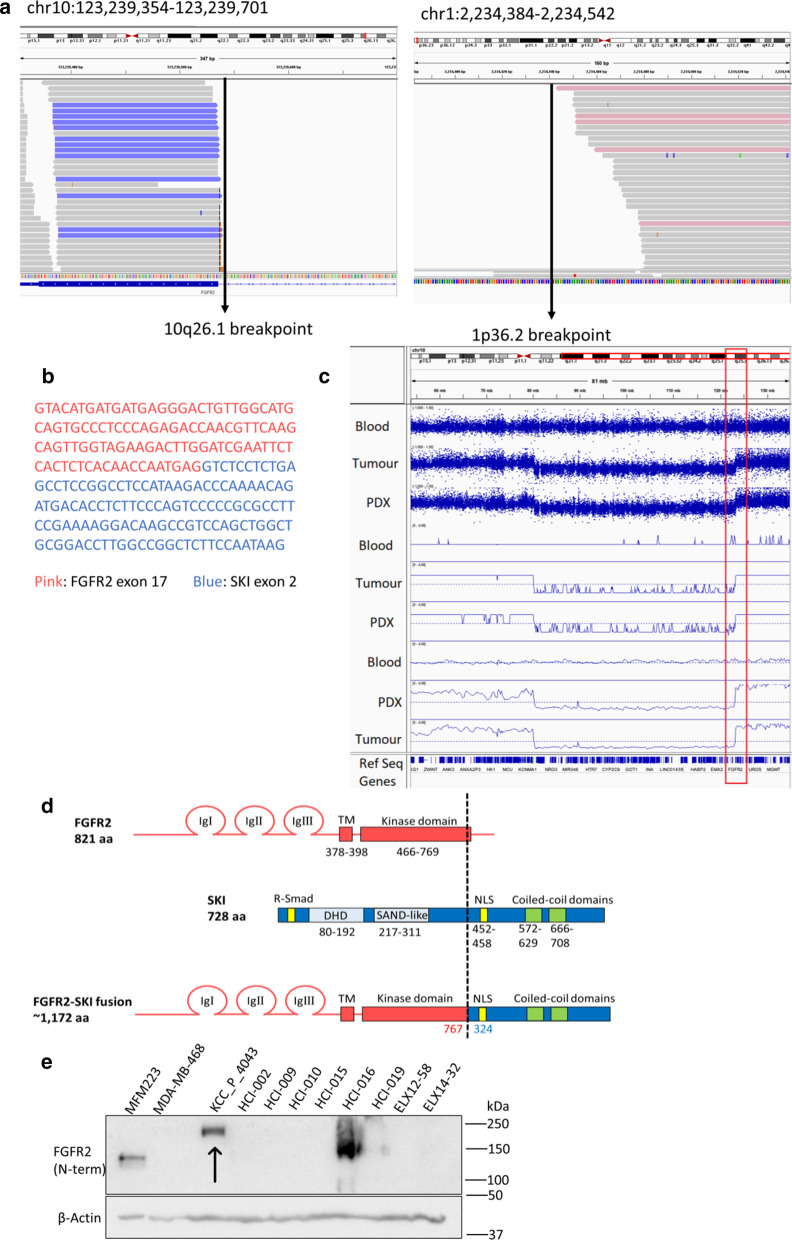
Fig. 3.
Characterization of the FGFR2-SKI fusion identified in the KCC_P_4043 PDX model. a Integrative Genomic Viewer results for breakpoint regions of chromosome 10 (containing FGFR2) and chromosome 1 (SKI). b Junction break point sequence of FGFR2-SKI fusion. Pink, FGFR2 exon 17; blue, SKI exon 2. c Analysis of FGFR2 in the KCC_P_4043 using SNP arrays. Top three tracks are copy number raw logRatio data from the array; middle three tracks are copy number segmentation from the raw logRatio; bottom three tracks are smoothed copy number signal. The red box highlights FGFR2 on chromosome 10. d Schematic of the FGFR2-SKI fusion in KCC_P_4043. Domain structure and amino acid residues of FGFR2 and SKI are indicated. In FGFR2, IgI–IgIII: immunoglobulin 1–3. TM: transmembrane domain. In SKI, R-smad: corresponding binding domain. DHD: Dachshund homology domain. SAND: Sp100, AIRE1, NucP41/75 and DEAF1. NLS: nuclear localization sequence. The dotted line highlights the junction between FGFR2 and SKI. e Confirmation of FGFR2-SKI expression by Western blotting. Protein lysates from 9 PDX samples were immunoblotted with a FGFR2 N-term antibody. MFM-223 and MDA-MB-468 lysates were used as positive and negative controls, respectively