Figure 4.
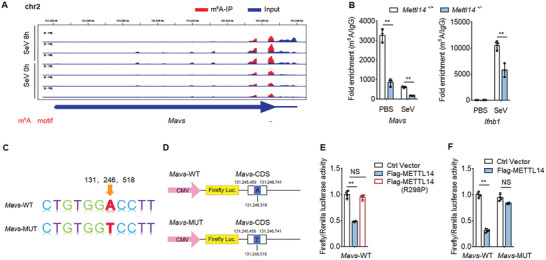
METTL14 catalyzes m6A modification of Mavs mRNA. A) RNA‐seq of Mavs mRNA in input RNA and m6A immunoprecipitated RNA from peritoneal macrophages infected with SeV for 8 h; m6A motif sequences that correspond to an immunoprecipitate‐enriched region are marked in red. B) The enrichment of MAVS mRNA in Mettl14 +/+ and Mettl14 +/− macrophages with anti‐m6A antibody, followed by m6A‐RIP‐qPCR analysis, with IgG as a negative control. C) Schematic plot of the Mavs‐WT or Mavs‐MUT mRNA nucleotide sequence. D) Schematic plot of the luciferase reporter of Mavs‐WT or Mavs‐MUT. E) Relative luciferase activity of Mavs‐WT was measured after cotransfection with Flag‐METTL14, Flag‐METTL14‐R298P, or control vector in HEK293T cells. Cell lysis was quantified for firefly luciferase activity, with the normalization to Renilla luciferase activity as an inner control. F) Relative luciferase activity of Mavs‐WT and a mutant vector carrying mutation in the m6A site were measured after cotransfection with Flag‐METTL14 or control vector in HEK293T cells. Cell lysis was quantified for firefly luciferase activity, with the normalization to Renilla luciferase activity as an internal control. Data information: Data are presented as mean ± S.D. Two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS: no significance (B,E,F).
