Figure 1.
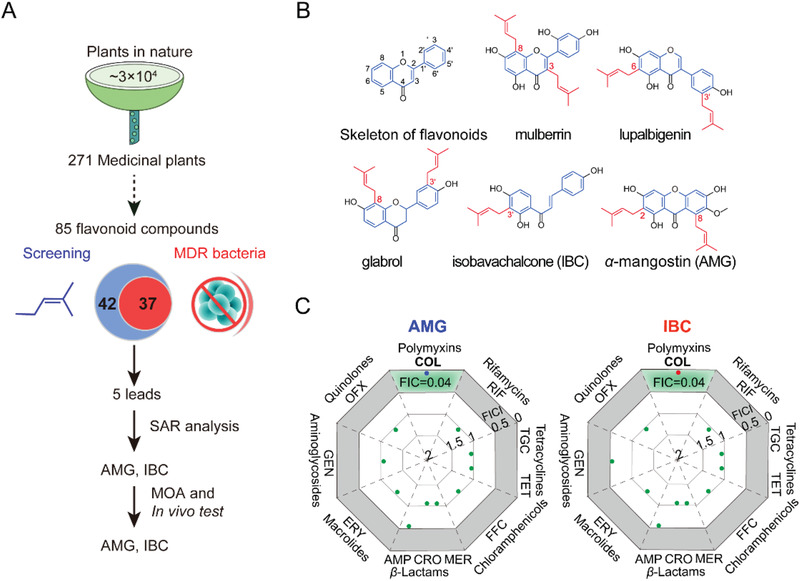
AMG and IBC show robust antibacterial activity against Gram‐positive bacteria and reverse colistin resistance in Gram‐negative bacteria. A) The scheme of screening antibacterial compounds in this study. 85 flavonoid compounds derived from 271 medicinal plants were collected and the antibacterial activities against Gram‐positive and Gram‐negative bacteria were determined by the broth micro‐dilution method according to the CLSI 2021 guideline. The SAR was analyzed and potent antibiotic candidates were chosen. Finally, the mode of action (MOA) and efficacy in vivo were clarified. B) Chemical structures of the skeleton of flavonoids and the five lead compounds; the skeleton of flavonoids was marked in blue and the isopentenyl group was in red. C) Synergy of AMG or IBC with different classes of antibiotics against E. coli B2. FICI were determined by chequerboard microdilution assays. Synergy is defined as a FICI ≤ 0.5. AMP, ampicillin; CRO, ceftriaxone; MER, meropenem; ERY, erythromycin; GEN, gentamicin; OFX, ofloxacin; COL, colistin; RIF, rifampicin; TGC, tigecycline; TET, tetracycline; and FFC, florfenicol. Data represent two biological replicates.
