Figure 2.
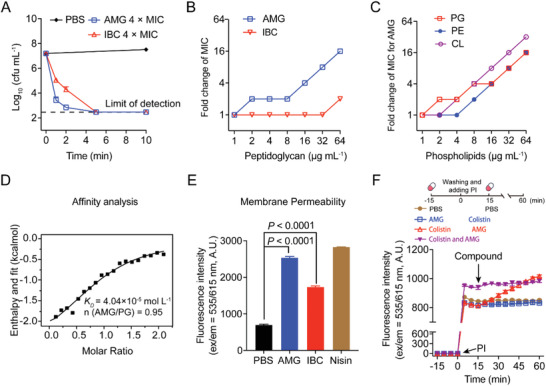
AMG and IBC exert antibacterial effects through membranes. A) Time‐kill curves of AMG and IBC against S. aureus ATCC 29213 in the exponential phase at 37 °C. 4 × MIC of AMG, IBC killed the bacteria rapidly. B) Exogenous addition of peptidoglycan from S. aureus decreased the antibacterial activities of AMG and IBC determined by chequerboard microdilution assays. The concentration of peptidoglycan was in the range of 0 to 64 µg mL−1. C) Exogenous addition of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), and cardiolipin (CL) abolished the antibacterial activity of AMG against S. aureus ATCC 29213, determined by chequerboard microdilution assays. The concentrations of phospholipids were in the range of 0 to 64 µg mL−1. D) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) analysis of the interaction between PG and AMG. Thermodynamic parameters were calculated, including equilibrium dissociation constant (K D = 4.04 × 10−5 mol L−1), number of binding sites (n = 0.95), molar binding enthalpy (ΔH = −11.87 kJ mol−1), and molar binding entropy (ΔS = 44.28 J mol−1 K−1). E) Increased membrane permeability after treatment of AMG or IBC at 4 × MIC. The membrane permeability was determined by propidium iodide (PI) with the excitation/emission wavelength at 535 nm/615 nm. F) The dynamic curves of the permeability of inner membrane probed with PI for E. coli B2, under the treatments of AMG, and colistin and both thereof. E. coli B2 were incubated with different antibacterial drugs at 37 °C for 15 min. After washing for three times, PI was added and the fluorescence was determined for 15 min. Then the other drugs were added. The fluorescence was measured with the excitation wavelength at 535 nm and emission wavelength at 615 nm. The concentrations of AMG and colistin were 2 and 0.25 µg mL−1, respectively. All experiments in A, E, and F were performed as three biologically independent experiments, and the mean ± s.d. is shown, n = 3. Data in (B,C) represent two biological replicates. P values in E were determined using unpaired student's t‐test.
