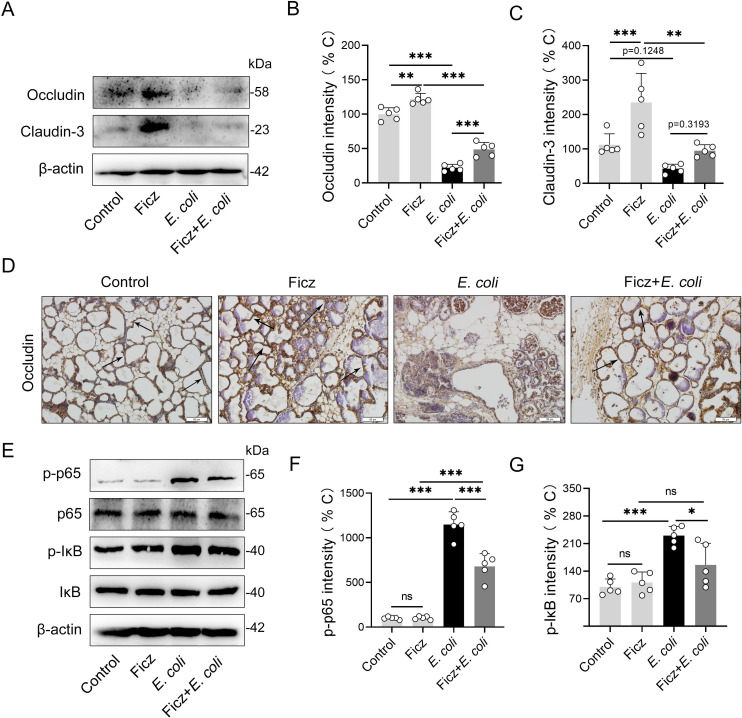
Fig 2. AhR activation by Ficz improves barrier integrity and limits inflammatory signaling in mice with E. coli-induced mastitis.
Mice were treated with or without Ficz (1 μg/mouse) intraperitoneally 1 h before the E. coli was applied (107 CFU/50 μL each breast duct). Twenty-four hours later, the mammary gland tissues were harvested and detected. (A-C) The levels of tight junction proteins, including occludin and claudin-3, in mammary glands were detected using western blots (n = 5). (D) Representative images of mammary gland immunohistochemistry (IHC) sections stained with occludin antibody (scale bar, 50 μm). The black arrow indicates the positive staining. (E-G) Protein levels of the NF-κB signaling pathway, including phosphorylated p65 and IκB, as well as p65 and IκB, which were measured by western blotting (n = 5). One-way analysis of variance was applied for statistical analysis of (B-C) and (E-F) and the date are presented as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 mean significant differences from each group. ns, no significance.