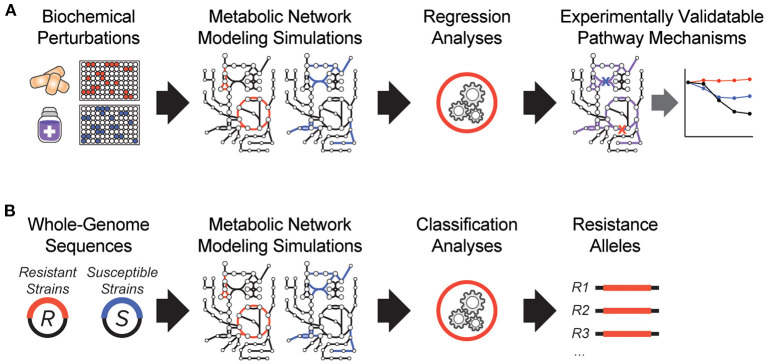
Figure 1.
Recent innovations in interpretable machine learning for studying antibiotic treatment failure. (A) A biochemical screen was combined with metabolic network modeling and machine learning regression analyses to elucidate pathway mechanisms of antibiotic lethality. This led to the discovery that purine biosynthesis is a critical component of bactericidal antibiotic lethality (9). (B) Whole-genome sequencing data from antibiotic resistant (R) and susceptible (S) strains from clinical strains were applied as modeling constraints to genome-scale metabolic models. Machine learning classification analyses were applied (10).