Figure 3.
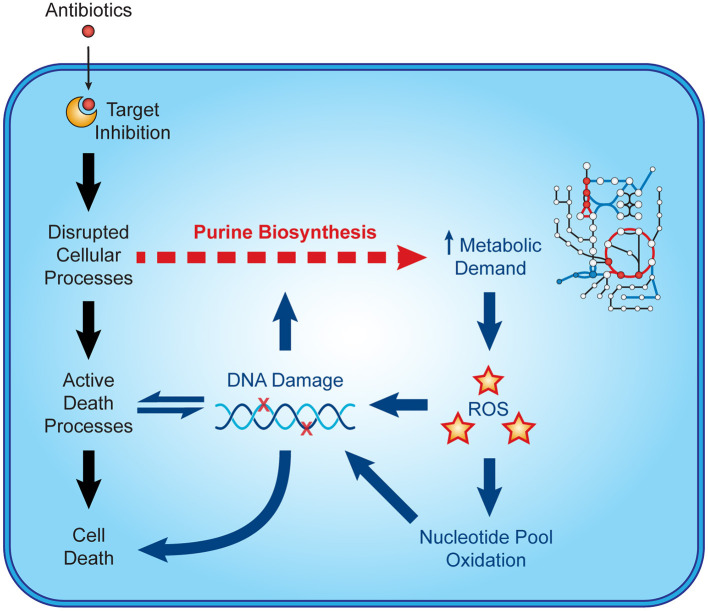
Nucleotide metabolism contributes to antibiotic lethality. In addition to their target-specific effects, bactericidal antibiotics induce purine biosynthesis, which increases activity in central metabolism. Increases in central metabolism stimulate the production of toxic reactive oxygen species, which oxidize nucleotides and damage DNA. These insults to DNA and the nucleotide pool induce bacterial death and may further potentiate purine biosynthesis.