Fig. 5. PBC micelles serve as a platform for in vitro therapeutic antibody production.
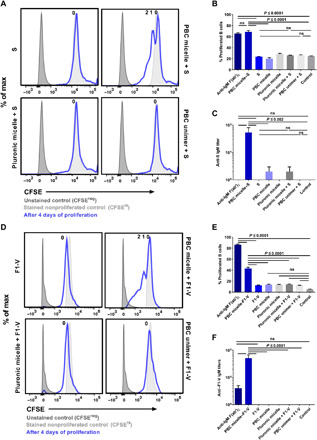
Splenic cell population obtained from WT C57BL/6 mice or BALB/c mice following RBC lysis was stimulated in 96-well U-bottom plates at a density of 0.5 × 106 per well. Anti-CD40 (5 μg/ml) was added to all the treatment groups except unstimulated controls. S protein from SARS-CoV-2 (10 μg/ml) and F1-V from Y. pestis (10 μg/ml) was used with or without PBC micelles (10 μg/ml), Pluronic F127 micelles (10 μg/ml), or PBC unimers (10 μg/ml). (A) Histograms depicting CFSE levels of B cells stimulated with various treatment groups with or without S protein for 4 days. (B) Percent proliferated viable B cells as determined by CFSElo gating. (C) Anti-S IgM titers measured in the supernatants of the stimulated cells after 10 days. (D) Histograms depicting CFSE levels of B cells stimulated with various treatment groups with or without F1-V for 4 days. (E) Corresponding percent proliferated viable B cells as determined by CFSElo gating. (F) Anti–F1-V IgM titers measured in the supernatants of the stimulated cells after 10 days. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 2 to 4. PBC micelle, S protein, F1-V, Pluronic F127 micelle, and PBC unimers are not significant from medium-only control.
