Fig. 7. GRB2 KO sensitizes cells to PARPi.
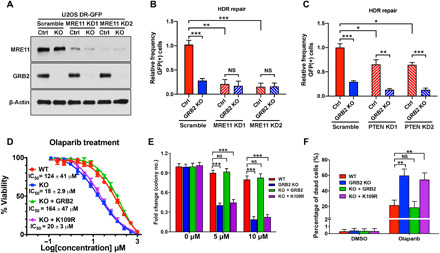
(A) MRE11 depletion levels with two different shRNA (KD1 and KD2) in U2OS cells with normal level of GRB2 (Ctrl) and GRB2-KO. (B) DR-GFP reporter assay in MRE11-KD control (Ctrl) and GRB2-KO U2OS cells. (C) DR-GFP reporter assay in PTEN-KD and/or GRB2-KO U2OS cells. (D) Sulforhodamine B assay of olaparib-induced cytotoxicity in control HeLa cells, GRB2-KO cells, and GRB2-KO cells reconstituted with WT or K109R mutant GRB2. IC50 values are shown. (E) Clonogenic assay evaluating the effect of a PARPi on colony formation of HeLa cells. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of the PARPi olaparib and cultured for 10 days, and then the resulting colonies were visualized with crystal violet staining and counted by GelCount instrument. Parental control (WT), GRB2-KO (KO), WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2), and K109RGRB2 (KO + K109R) reconstituted HeLa cells. (F) Bar graph representing annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) combined labeling and flow cytometry analysis of olaparib-treated control (WT), GRB2-KO, reconstituted WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2), and K109R mutant (KO + K109R) HeLa cells. Cells were treated with either dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 50 μM olaparib for 72 hours. All data are representative of three independent experiments. The significance was analyzed by two-sided Student’s t test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001; NS, not significant.
