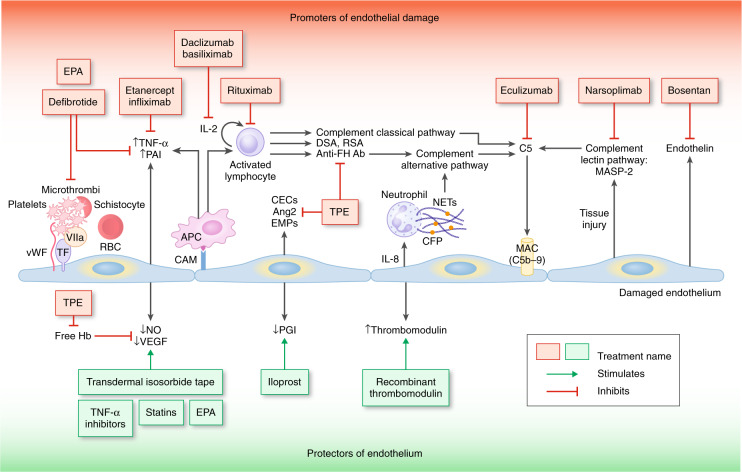
Fig. 1. Pathophysiology of TA-TMA with the sites of action of proposed treatments.
The illustration is separated into two halves. The upper half demonstrates the numerous mechanisms that promote endothelial damage and the treatments targeting these promoters of injury. The lower half represents the effect the damaged endothelium has on protective factors of the endothelium and the treatments, which enhance these cytoprotective factors. Therapies shown as potential treatment options but have not been widely or rigorously studied include EPA, TNF-α inhibitors (etanercept, infliximab), bosentan, transdermal isosorbide tape, statins, iloprost, and recombinant thrombomodulin. Adapted with copyright permission from Fig. 4 Khosla et al. [101]. Ang2 angiopoietin 2, APC antigen-presenting cell, CAM cell adhesion molecules, CEC circulating endothelial cell, CFP complement factor P, DSA donor-specific antibodies, EMP endothelial microparticles, EPA eicosapentaenoic acid, FH Factor H, Hb hemoglobin, IL interleukin, MAC membrane attack complex, MASP-2 mannose-binding protein-associated serine protease-2, NETs neutrophil extracellular traps, NO nitric oxide, PAI plasminogen-activator inhibitor, PGI2 prostacyclin, RBC red blood cell, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor alpha, RSA recipient-specific antibodies, TF tissue factor, TPE therapeutic plasma exchange, VIIa Factor VIIa, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, vWF von Willebrand factor.