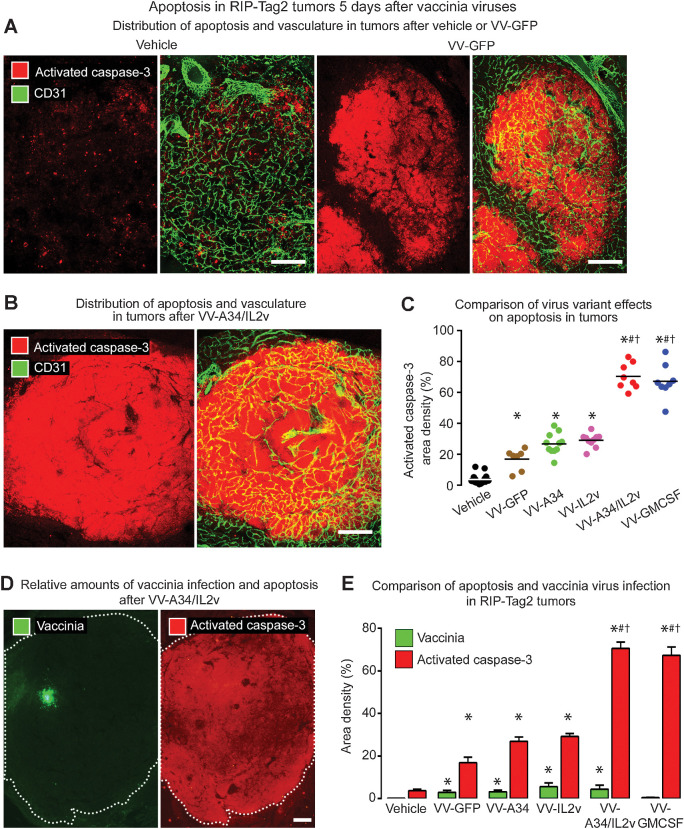
Figure 4.
Apoptosis in RIP-Tag2 tumors 5 days after vaccinia virus variants. A and B, Staining for apoptosis (activated caspase-3, red) and blood vessels (CD31, green). A, Confocal microscopic images show little apoptosis after vehicle, widespread apoptosis after reference virus VV-GFP, and even more extensive apoptosis after combination virus VV-A34/IL2v. B, Widespread apoptosis after VV-A34/IL2v. C, Activated caspase-3 in tumors of each mouse after virus or vehicle. Values after VV-GFP or A34K151E substitution virus VV-A34 were similar to one another but significantly greater than after vehicle. By comparison, values after VV-A34/IL2v or VV-GMCSF were significantly greater than after the other viruses. D, Fluorescence microscopic images of tumor after VV-A34/IL2v compare focal staining for vaccinia (green) to widespread staining for activated caspase-3 (red) in adjacent sections (white dotted line outlines tumor border). E, Staining for vaccinia (green bars) and activated caspase-3 (red bars) after vehicle and five virus variants show consistently larger amounts of apoptosis than vaccinia infection, where the ratios ranged from 6 for VV-GFP, to 16 for VV-A34/IL2v, to 143 for VV-GMCSF. ANOVA: P < 0.05 compared with vehicle*, VV-GFP#, or VV-IL2v†. Vehicle (N = 18), VV-GFP (N = 7), VV-A34 (N = 11), VV-IL2v (N = 10), VV-A34/IL2v (N = 8), VV-GMCSF (N = 8). Scale bar, 200 μm in all images.