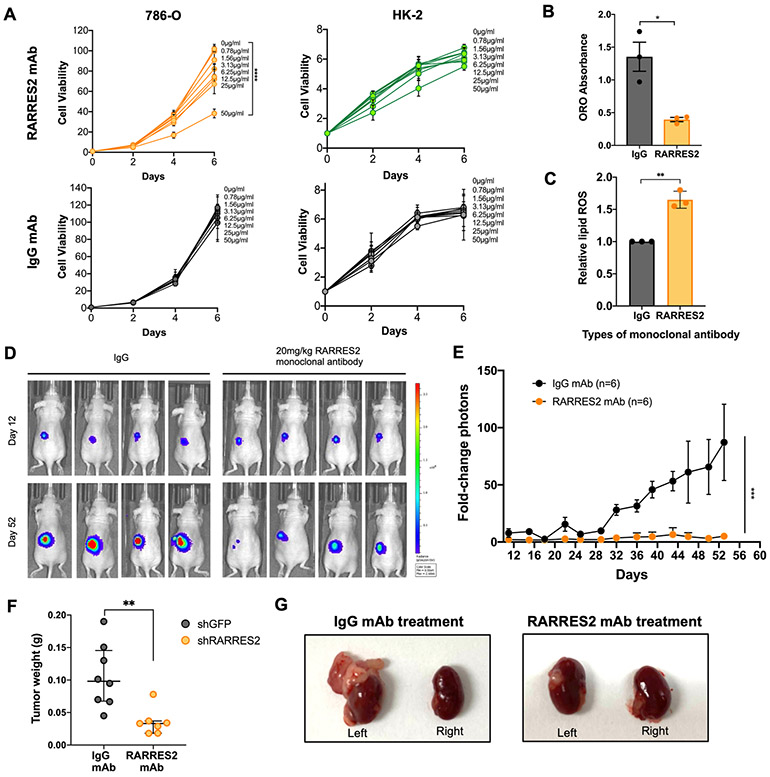
Figure 7. Monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting chemerin reduces ccRCC tumor burden.
(A) Cell viability assay of 786-O and HK-2 cells treated with RARRES2 mAb (upper panels) and IgG mAb control (lower panels). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA was used for statistical analysis with Tukey correction.
(B) ORO staining quantification in 786-O cells treated with either IgG mAb or RARRES2 mAb. Two tailed student’s t-test.
(C) Relative lipid ROS measured using BODIPY 581/591 C11 assay in 786-O cells treated with either IgG mAb or RARRES2 mAb. Two tailed student’s t-test.
(D) Representative bioluminescence imaging of before (Day 0) and Day 28 post-treatment in mice receiving 20 mg/kg of either mAb (n=6 each arm), after 786-O was implanted orthotopically under the left kidney capsule of nude mice.
(E) Quantification of bioluminescence imaging of before (day 0) and day 52 post-treatment in mice receiving 20 mg/kg of either mAb (n=6 each arm), after 786-O cells were implanted orthotopically under the left kidney capsule of nude mice. One-tailed student’s t-test.
(F) Tumor weight measurement (n=6 each group) at the end of the assay. Student’s t-test.
(G) Representative kidney tumor from (E).
Error bars represent SEM of three independent experiments and three technical replica per experiment. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.