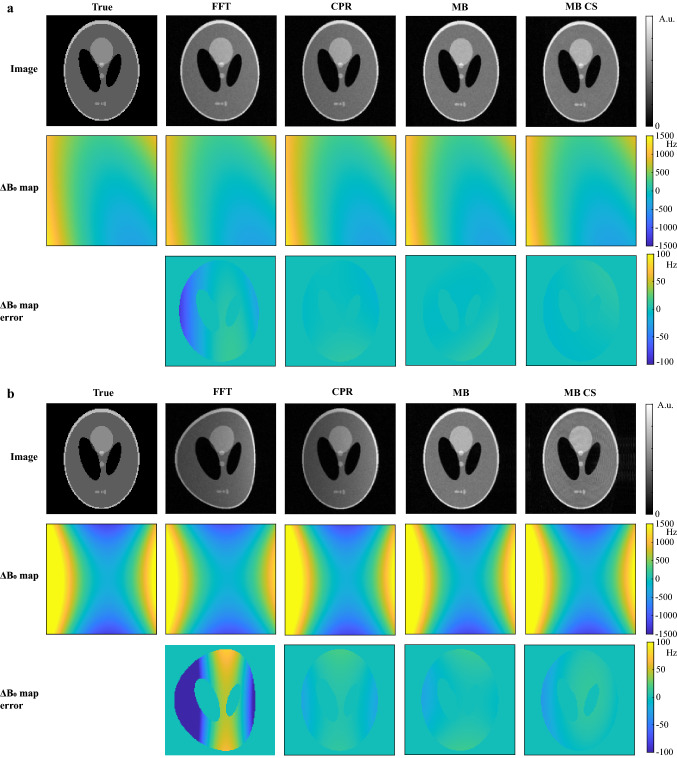
Fig. 2.
Comparison of FFT, iterative MB and iterative CPR approaches for simulation data in the center slice and in an off-center slice. a Center slice. (Top row) The FFT reconstruction results in a slight stretch of the Shepp–Logan phantom along the readout direction (left-to-right). (Middle row) The standard mapping technique (FFT) leads to inaccuracies in regions where the inhomogeneities are strongest (~ 600 Hz). The iterative CPR and MB approaches correct for this stretch using the estimated field map in each iteration and result in very similar image quality and maps. (Bottom row) This is confirmed by the low errors in the estimated maps. The MB CS reconstruction for an undersampling factor of 2 shows very similar errors to that of the MB approach. b Off-center slice. The stronger inhomogeneities in this slice (~ 1500 Hz) result in even larger errors using the standard mapping technique (FFT). Iteratively applying CPR and MB reduces the errors. For iterative MB image reconstruction, the uniformity of the image is closer to that of the true object compared to iterative CPR