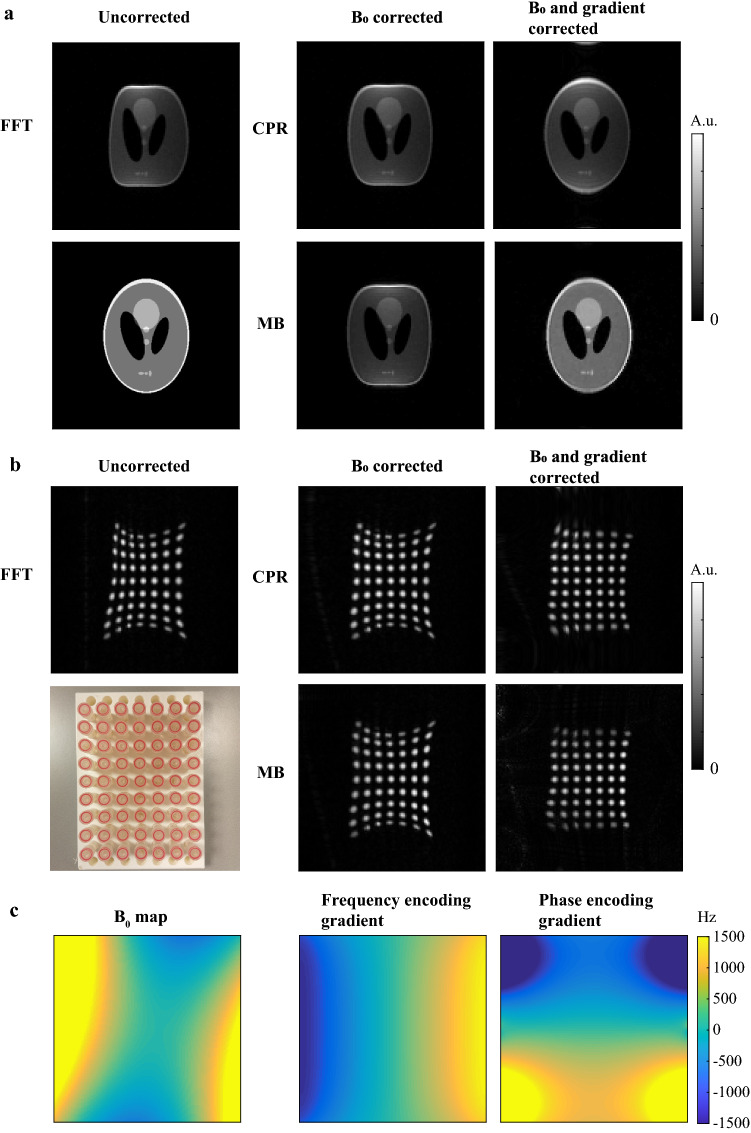
Fig. 5.
Combined gradient nonlinearity and correction for simulation and measurement data. a Gradient nonlinearities produce additional image distortions on top of -induced image distortions for a simulated Shepp–Logan phantom when reconstructed with an FFT. Iterative CPR and iterative MB are able to correct for both type of distortions simultaneously, but iterative MB shows a more uniform signal intensity compared to iterative CPR. b Measurement data of a rectangular grid phantom, containing 63 equally spaced tubes filled with sunflower oil, show reduced and gradient distortions when reconstructed with iterative MB and CPR. Residual image distortions in measurement data are potentially caused by small differences between simulated gradient maps and actual gradient fields, which could, for example, arise when one of the gradient coils is slightly rotated with respect to its orthogonal position. A photograph of the phantom is shown in the lower-left corner. c The map was estimated from the measured data in (b), and subsequently used to simulate image distortions in (a). Maps of the frequency and phase encoding gradients were simulated in coronal orientation using Biot–Savart’s law