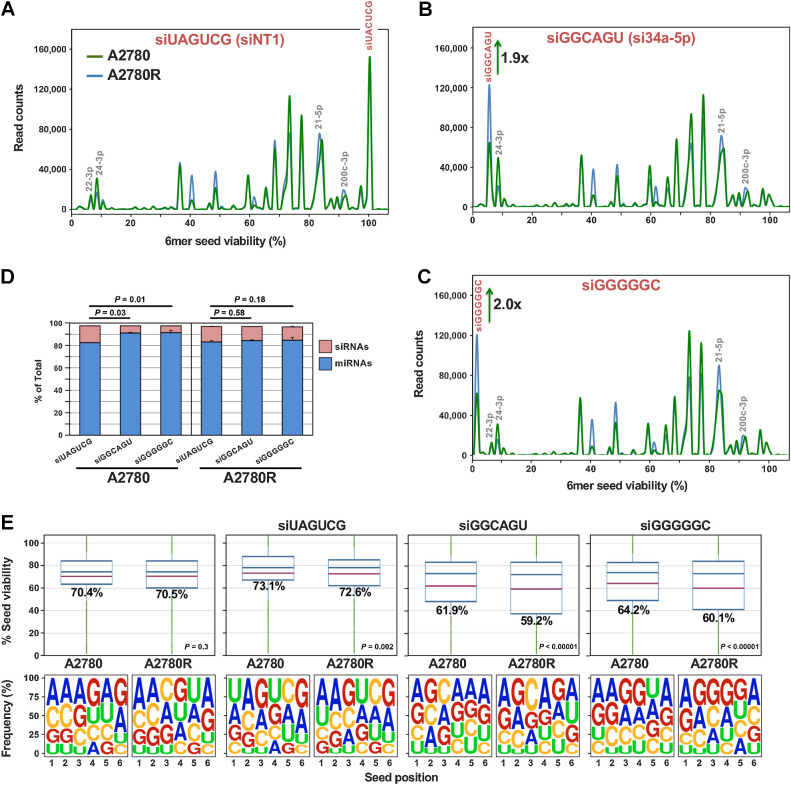
Figure 4.
Platinum-resistant A2780R cells have more toxic miRNAs in their RISC than sensitive A2780 cells. A–C, Seed tox graph of RISC-bound miRNAs and exogenous siRNAs in A2780/A2780R cells 24 hours after transfection with either the nontoxic siUAGUCG (siNT1), or the highly toxic siGGCAGU, or siGGGGGC. D, Percent miRNAs and exogenous siRNAs in the RISC of the siRNA-transfected cells. Student test P values are shown on the change in percent of transfected siRNAs. E, Average seed tox (top) and seed composition (bottom) of all RISC-bound sRNAs in A2780/A2780R cells PBS treated or treated with the three siRNAs. P values were calculated using a Wilcoxon rank test. The fraction of exogenous siRNAs and endogenous miRNAs was approximately 97% in all samples.