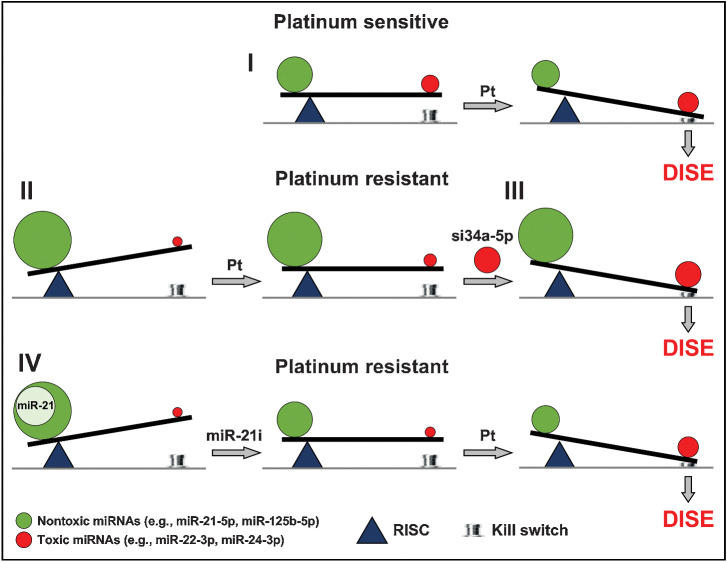
Figure 7.
Scheme to illustrate the balance of toxic RISC-bound miRNAs that determine platinum sensitivity. In constitutively Pt-S ovarian cancer cells, treatment with Pt results in a shift in the ratio of miRNAs with toxic and nontoxic seeds tipping the balance toward cell death (death induced by survival gene elimination, DISE; I). In ovarian cancer cells with acquired Pt resistance, the shift toward toxic seed–containing miRNAs is insufficient to trigger DISE (II). However, the protection by miRNAs with nontoxic seeds can be overcome by introducing exogenous miRNA mimetics (e.g., siGGCAGU = si34a-5p) that contain highly toxic seeds (III). Finally, inhibiting miRNAs with nontoxic seeds, as shown for overexpressed miR-21-5p (using a miR-21-5p inhibitor, miR-21i) in the A2780R cells, allows the Pt-R cells (both constitutively as well as acquired) to regain sensitivity to Pt (IV).