Figure 2.
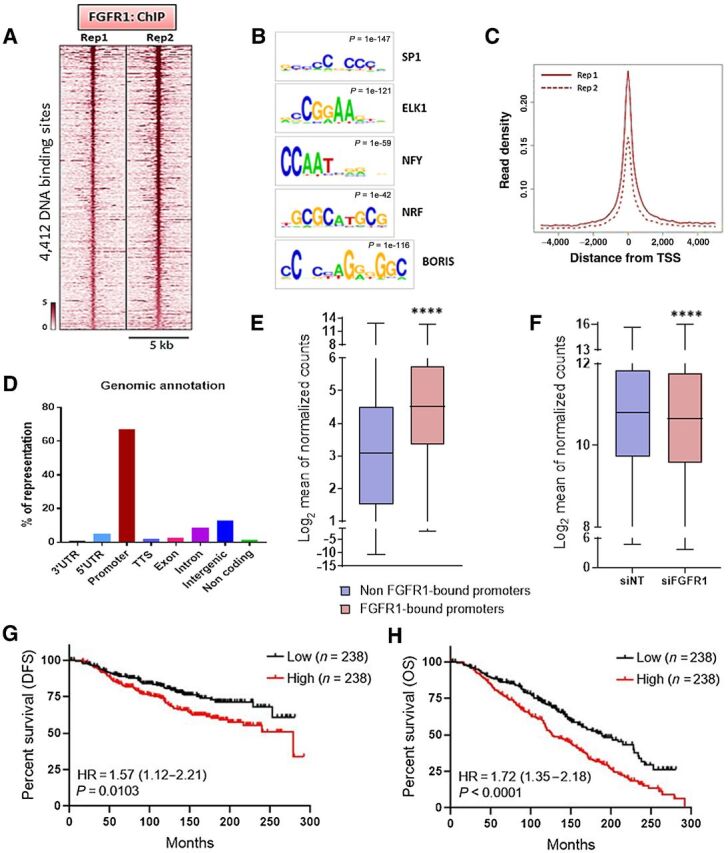
Nuclear FGFR1 occupies chromatin at TSSs of genes associated with antiestrogen resistance. A, Heatmap showing ChIP-seq read densities around the FGFR1-bound regions in CAMA1 cells, in two replicates. The x-axis represents read densities within 5-kb region around the peak summit; the y-axis represents each predicted binding site. Cells were cultured for 48 hours in IMEM/10% CSS. B, Top consensus motifs, identified by de novo motif analysis, at genomic loci bound by FGFR1 identified in A. Statistical significance expressed as P value for each motif is shown. C, Plot representing the density of the FGFR1 distribution around the TSSs in the two ChIP-seq replicates. D, Genomic annotations for the FGFR1-binding sites identified by ChIP-seq showing enrichment of promoter regions. E, Expression level of genes whose promoter is bound by FGFR1 (red; 2,704 genes) versus gene expression of all other genes (blue; 10,452 genes). Data are derived from RNA-seq on CAMA1 cells cultured for 48 hours in IMEM/10% CSS (**** P < 0.0001, Mann–Whitney test). F, Gene expression of genes whose promoter is bound by FGFR1 in CAMA1 cells upon siRNA-mediated FGFR1 knockdown (n = 3; **** P < 0.0001, two-tailed Wilcoxon test). G, Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (H) of the METABRIC cohort of 950 patients with ER+/HER2− breast cancer treated with antiestrogens as a function of the FGFR1-associated polygenic score (lowest quartile vs. highest quartile). The signature score was calculated by GSVA (77).
